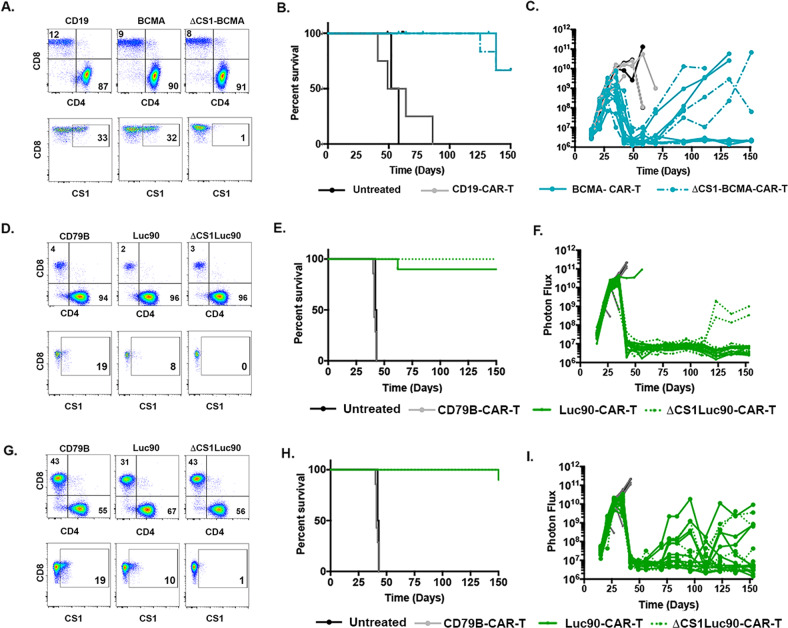
Fig. 3. Efficacy Luc90-CAR-T is independent of CD4:CD8 ratio.
A Flow cytometry was used to assess CD4 and CD8 percentages in CAR-T cultures as shown. Data shown are sorted CAR + cells B Kaplan–Meier Survival of mice treated with CD19-CAR-T (n = 4), BCMA CAR-T (n = 8, 4 were tumor free and censored due to infection at housing facility), ΔCS1-BCMA-CAR-T (n = 9, 3 were tumor free and censored due to infection at housing facility) or left untreated (n = 2). C Bioluminescent imaging. Each line represents one mouse. D Flow cytometry was used to assess CD4 and CD8 percentages in CAR-T cultures as shown that were designed to have a high CD4:CD8 ratio. Data shown are sorted CAR + cells. E Survival and (F) BLI of mice treated with Luc90-CAR-T (n = 10), ΔCS1 Luc90-CAR-T (n = 10), CD79B CAR-T (n = 3) and untreated mice (n = 2). G Flow cytometry showing CD4 and CD8 percentages of CAR-T as shown generated to have a lower CD4:CD8 ratio. H Survival and (I) tumor burden (BLI) in mice treated with Luc90-CAR-T (n = 10), ΔCS1 Luc90-CAR-T (n = 10), CD79B CAR-T (n = 3) and untreated mice (n = 2). Although graphed separately, survival plots show same control mice (CD79B and untreated) since experiment was performed at same time.