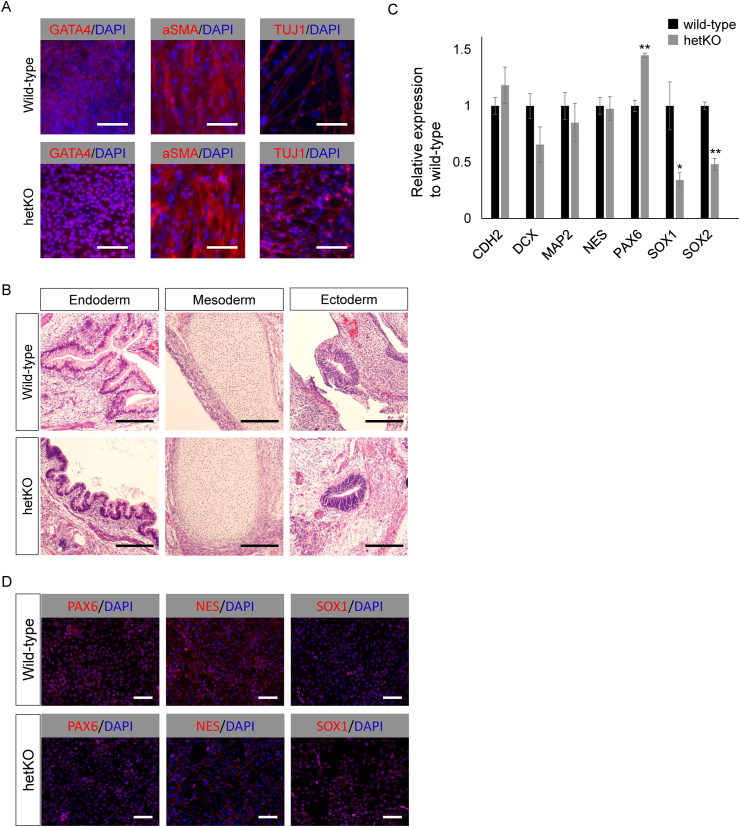
Fig. 3.
Both control isogenic line and hsa-miR-302/367 cluster heterozygous knockout Edom_iPSCs can differentiate into three germ layers. (A) Both the control isogenic line and Homo sapiens (hsa)-miR-302/367 cluster heterozygous knockout Edom_iPSCs differentiated in vitro via EB adhesion culture. Both cell lines expressed markers of primary germ layers. Immunohistochemical analyses of markers of ectoderm (TUJ1), mesoderm (αSMA), and endoderm (GATA4) layers are shown. Scale bars are 100 μm. (B) Both the control isogenic line and hsa-miR-302/367 cluster heterozygous knockout Edom_iPSCs differentiated in vivo via teratoma formation. Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed germ layer derivatives, such as neural tissues (ectoderm; right panels), cartilage (mesoderm; middle panels), and gut epithelial tissues (endoderm; left panels). Scale bars are 100 μm. (C) Neural stem cell (NSC) marker genes were analyzed in NSCs derived from both a control isogenic line and hsa-miR-302/367 cluster heterozygous knockout Edom_iPSCs. CDH2, DCX, MAP2, and NES expression were comparable between heterozygous knockout and the control isogenic line. PAX6 was relatively high in the heterozygous knockout line, while SOX1 and SOX2 were relatively low. (D) Neural stem cell markers, including PAX6, NES, and SOX1, were normally expressed and localized in the heterozygous knockout Edom_iPSC and isogenic control lines. Scale bars are 100 μm. DAPI staining is shown in blue. hetKO, hsa-miR-302/367 cluster heterozygous knockout. ∗P < 0.05. ∗∗P < 0.01.