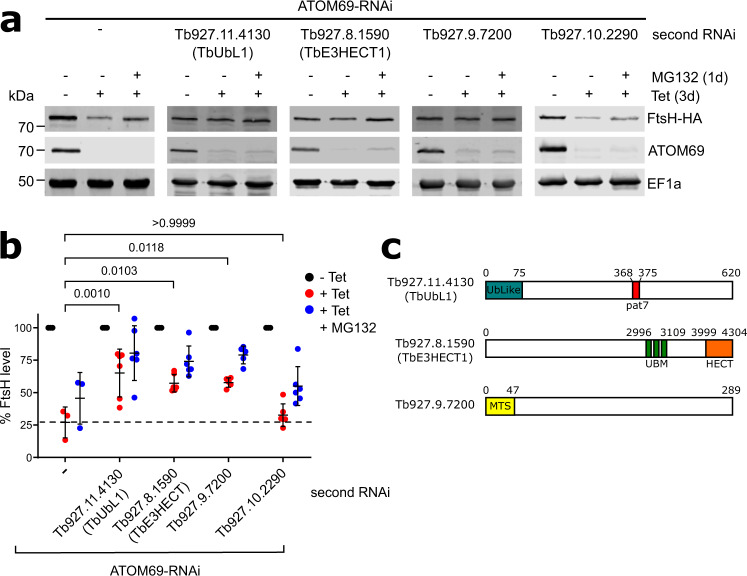
Fig. 3. Three recruited proteins have a role in mitochondrial quality control (MQC).
a Immunoblots depicting the change in abundance of a 3x HA-tagged model substrate FtsH (FtsH-HA) in whole cells. RNAi-mediated ablation of atypical translocase of the outer membrane 69 (ATOM69) by tetracycline (−/+ tet) was either performed alone (left panel), or in combination with RNAi-mediated ablation of each of the four candidate proteins (right panels), in the absence and presence of MG132 (1d, 500 nM). 2 × 106 cells were loaded per lane. elongation factor 1a (EF1a) is used as a loading control. b Densitometric quantification of the immunoblot signals of FtsH-HA in the RNAi cell lines shown in a. The signal in the uninduced RNAi cell lines (-Tet) was set to 100%. The level of FtsH-HA for each sample was normalised to its respective EF1a signal. Data are presented as mean values with error bars corresponding to the standard deviation of six independent biological replicates, except for the ATOM69-RNAi cell where three replicates were used. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni posthoc test to allow for multiple comparisons. The p values calculated are as indicated in the graph. c Predicted domain structure of the three candidate proteins that contribute to the MQC pathway. Tb927.11.4130, termed ubiquitin-like protein 1 (TbUbL1), contains an Ub-Like domain (blue) and a Pat7 monopartite NLS sequence (red). Tb927.8.1590, termed TbE3HECT1, contains three ubiquitin-binding motifs (green) and an E3 ligase C-terminal HECT domain (orange). Tb927.9.7200 contains a predicted N-terminal mitochondrial targeting signal (yellow). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.