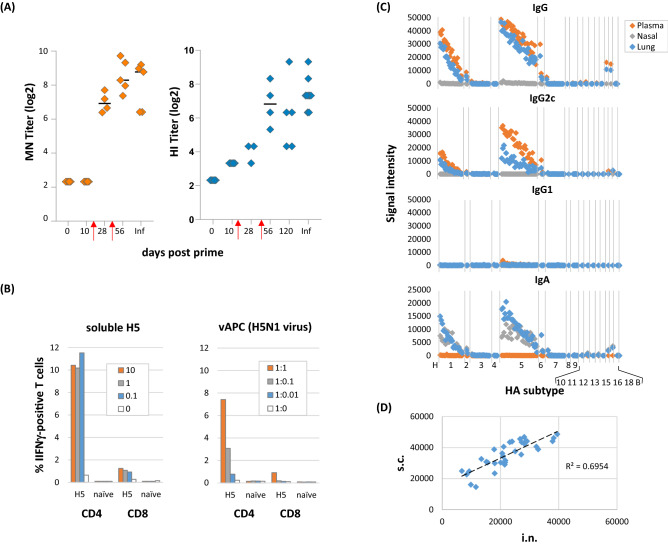
Figure 7.
Further characterization of H5/IVAX-1. Mice were administered trimerized H5 antigen from A/Viet Nam/1203/04 in combination adjuvant CpG/MPLA/AddaVax (“IVAX-1”). (A) Virus microneutralization (MN) and hemagglutination (HI) assays. Five C57Bl/6 mice were immunized and boosted on days 14 and d42 (red arrows), and plasma samples collected at different time points tested for neutralization against reassortant H5N1 virus. Plasma from H5N1-infected mouse (Inf) was used as a positive control. Neutralizing titers against H5N1 virus increase with boosting. (B) IVAX-1 preferentially stimulates CD4+ T cells compared to CD8+ T cells. T cell recall assays were performed by incubating splenocytes from H5/IVAX1-immunized mice with recall antigens as either soluble H5 protein (monomers from Sinobiological) at different concentrations (mg/mL), or syngeneic vAPCs (splenocytes exposed for 1 h to reassortant H5N1 influenza virus) at different splenocyte : vAPC ratios. Cultures were incubated overnight, and the proportions of IFNγ-positive CD4 and CD8 cells determined using ICS. (C) H5/IVAX-1 administered by intranasal (i.n.) route induces IgG2c in lung and plasma, and IgA in lung and nasal turbinate washes. B6 mice were administered H5 trimers in IVAX-1 adjuvant via the i.n. route on d0 and d56. Antibody profiling was performed on d69 using protein microarrays probed with plasma and lung and nasal washes. Antigens are ranked left-to-right in the same order in each panel indicating the IgG and IgA profiles are essentially identical. (D) Administration of H5/IVAX-1 via the i.n. route induces essentially identical profiles to administration via the s.c. route. Shown are scatter plots of Abs signals against different H5 variants on protein microarrays. Plasma samples were obtained after i.n. and s.c. administration (x and y axes, respectively); each point represents a different H5 drift variant.