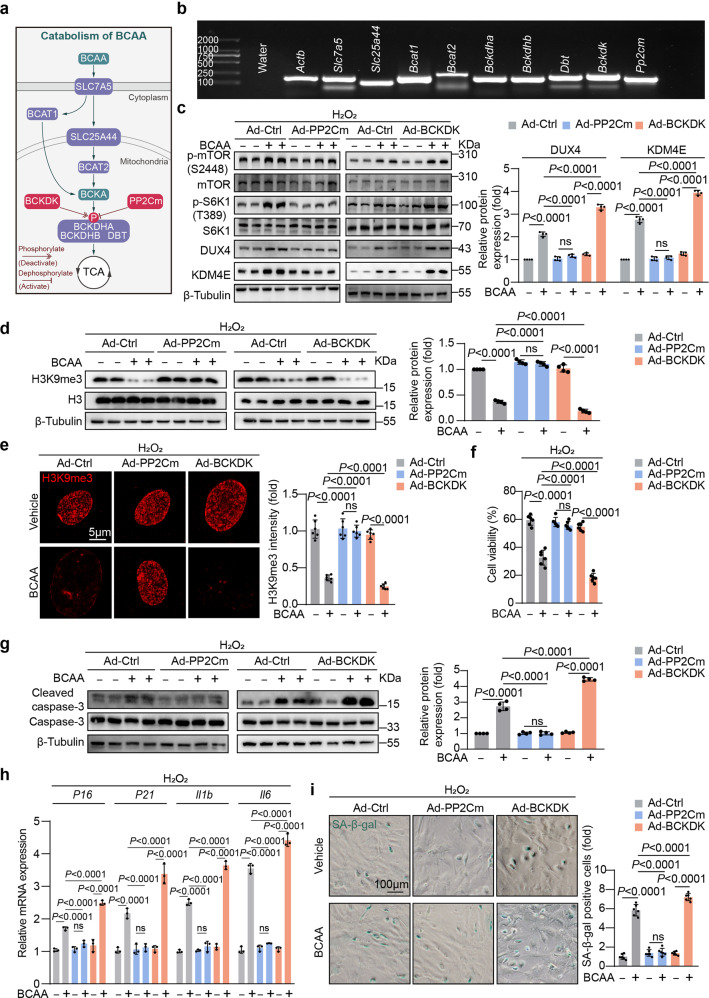
Fig. 6.
The BCAA catabolic capability of ADSCs determined their adaptation to the extracellular high BCAA milieu. a Schematic diagram of genes related to BCAA uptake, transportation, and catabolism. b mRNA levels of genes involved in BCAA metabolism measured by RT-PCR. Water was used as the negative control and Actb was used as the positive control. c ADSCs were transfected with control adenovirus (Ad-Ctrl), adenovirus overexpressing PP2Cm (Ad-PP2Cm) or adenovirus overexpressing BCKDK (Ad-BCKDK) and treated with or without BCAA (3.432 mM) in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (100 μM). Representative blots and quantification of p-mTOR (S2448), mTOR, p-S6K1 (T389), S6K1, DUX4, KDM4E, and β-tubulin as determined by western blot analysis. β-Tubulin was used as the loading control. d Representative blots and quantification of H3K9me3, histone H3, and β-tubulin. e Representative immunostaining images and quantification of H3K9me3. f ADSCs viability was determined by CCK-8 assay. g Representative blots of cleaved caspase-3, caspase-3, and β-tubulin. β-Tubulin was used as the loading control. h The mRNA levels of P16, P21, Il1b, and Il6 were analysed by RT-qPCR. i ADSC premature senescence was induced as methods described. Representative images and quantification of SA-β-gal positive cells. The data are shown as the means ± SD. The data were analysed by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. ADSCs adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells, BCAA branched chain amino acids, BCKDK BCKDHA kinase, DUX4 double homeobox protein 4, H3K9me3 histone H3K9 trimethylation, KDM4E lysine-specific demethylase 4E, mTOR the mechanistic target of rapamycin, PP2Cm mitochondrial matrix-targeted protein phosphatase 2C family member, SA-β-gal senescence-associated β-galactosidase, S6K1 ribosomal protein S6 kinase polypeptide 1