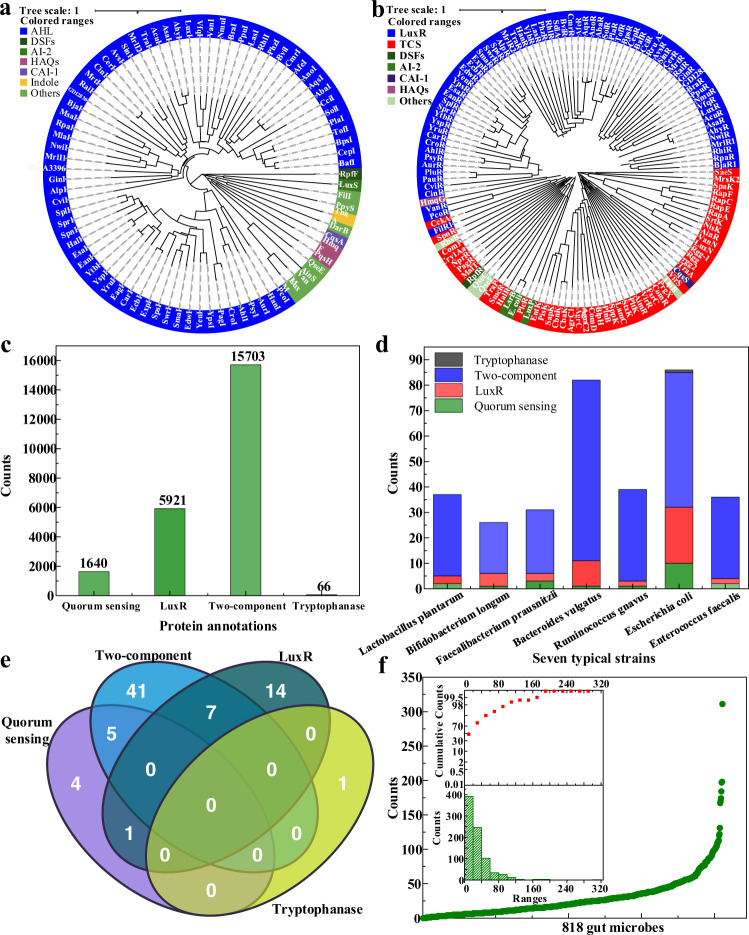
Fig. 2. Results of collections of the reported and annotated QS entries.
Evolutionary trees of QS synthases (a) and receptors (b). a The optimal tree with the sum of branch length = 40.33 is shown. This analysis involves 84 amino acid sequences, and there are a total of 1374 positions in the final dataset. b The optimal tree with the sum of branch length = 91.14 is shown. This analysis involves 129 amino acid sequences, and there are a total of 1010 positions in the final dataset. c Total QS&TCS entries with four protein annotations, i.e., “quorum sensing”, “LuxR”, “two-component”, and “tryptophanase”. d QS&TCS entries distribution of the seven-strain simplified human gut microbes used by Colosimo et al.42. e The overlap of the four types of QS&TCS entries in Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain. f QS&TCS entries count distribution of 818 human gut microbes from the VMH database28. Note that the subgraph indicates the cumulative distribution curve for the statistics of the collected QS&TCS entries. The upper and lower insets show the probabilities and histogram, respectively. “Ranges” in the subgraph shows the range of the number of QS&TCS entries contained in each strain. The “Counts” and “Cumulative counts” in the subgraph represents the specific number of strains and proportion, respectively. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.