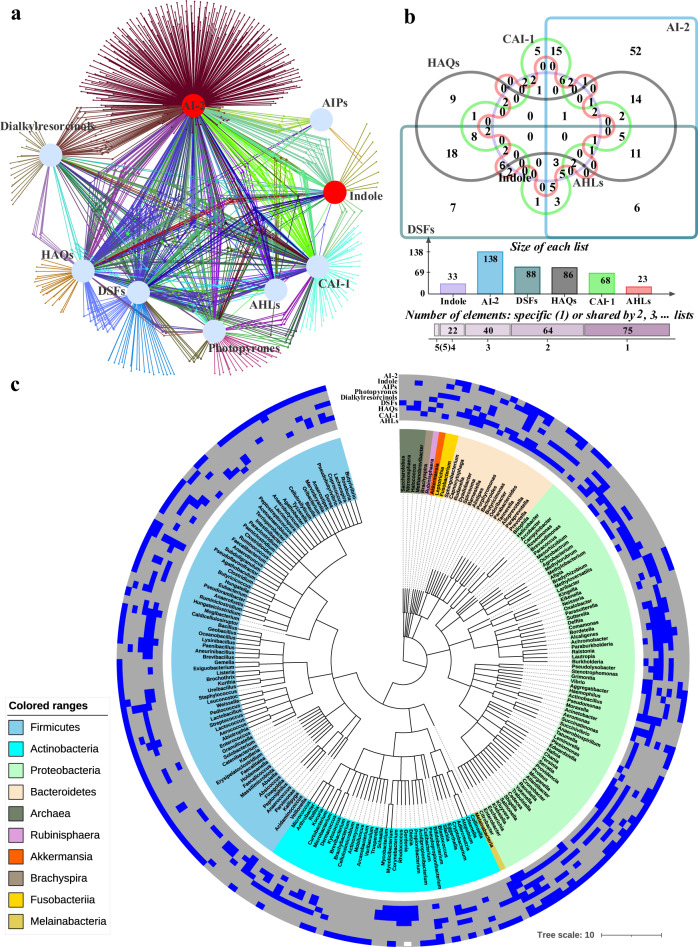
Fig. 5. QSCN for human gut microbiota based on diverse QS languages.
a QSCN for 818 human gut microbes based on nine languages (AHLs, DSFs, HAQs, CAI-1, AIPs, Dialkylresorcinols, Photopyrones, indole, and AI-2). Generally recognized intraspecies and interspecies languages are marked in blue and red, respectively. Note that the network diagram was generated using EVenn64. b Microbial genus distribution for six typical QS languages, i.e., AHLs, CAI-1, HAQs, DSFs, Indole, and AI-2. c Hierarchical clustering of nine QS languages found in 210 human gut microbial genus. The constructions are classified into ten genus-level clusters based on their phyla and taxonomy. Microbial genus from Firmicutes is colored in blue; Actinobacteria, cyan; Proteobacteria, green; Bacteroidetes, yellowish. Heatmap on the outermost layer indicates QS languages distribution in each cluster, existence is colored in blue; no existence, gray. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.