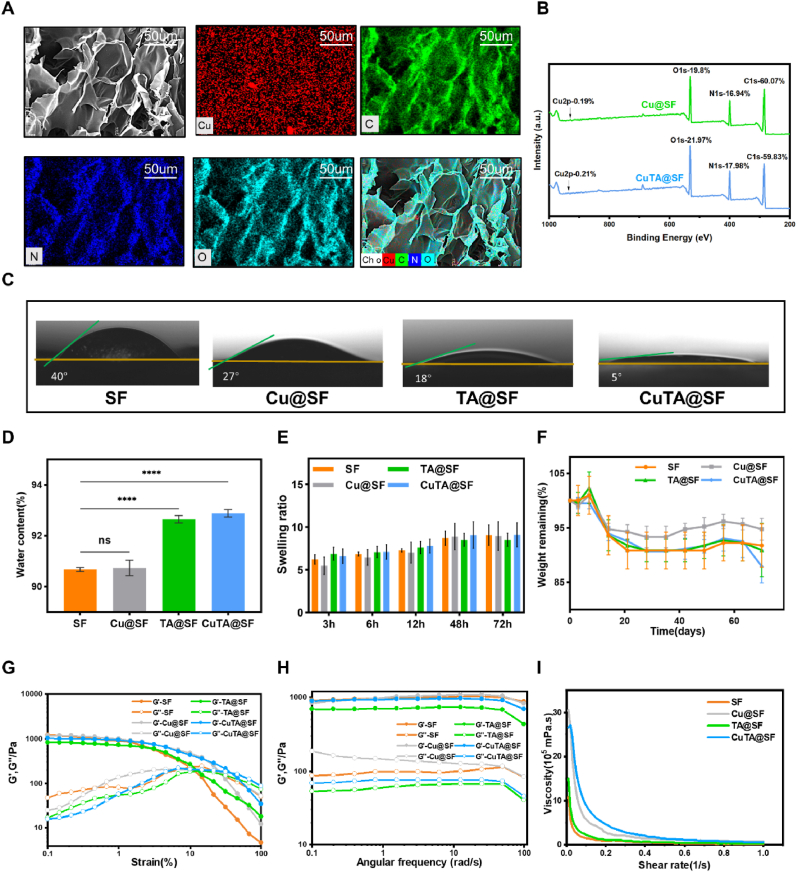
Fig. 2.
(A) The EDS-mapping analysis of CuTA@SF hydrogel. (B) Surface elemental analysis of Cu@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels with XPS. (C) The water contact angle of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels using deionized water. (D) The Equilibrium water content of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels. (E) The swelling ratio of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels in PBS at 37 °C. (F) In vitro degradation curves of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels in PBS at 37 °C. (G) Dynamic modulus of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels at varying stains from 0.1% to 100%. (H) Dynamic modulus of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels at varying angular frequency from 0.1 to 100 rad/s. (I) Viscosity-shear rate curves of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels. Results were shown as mean ± SD, ****p < 0.0001.