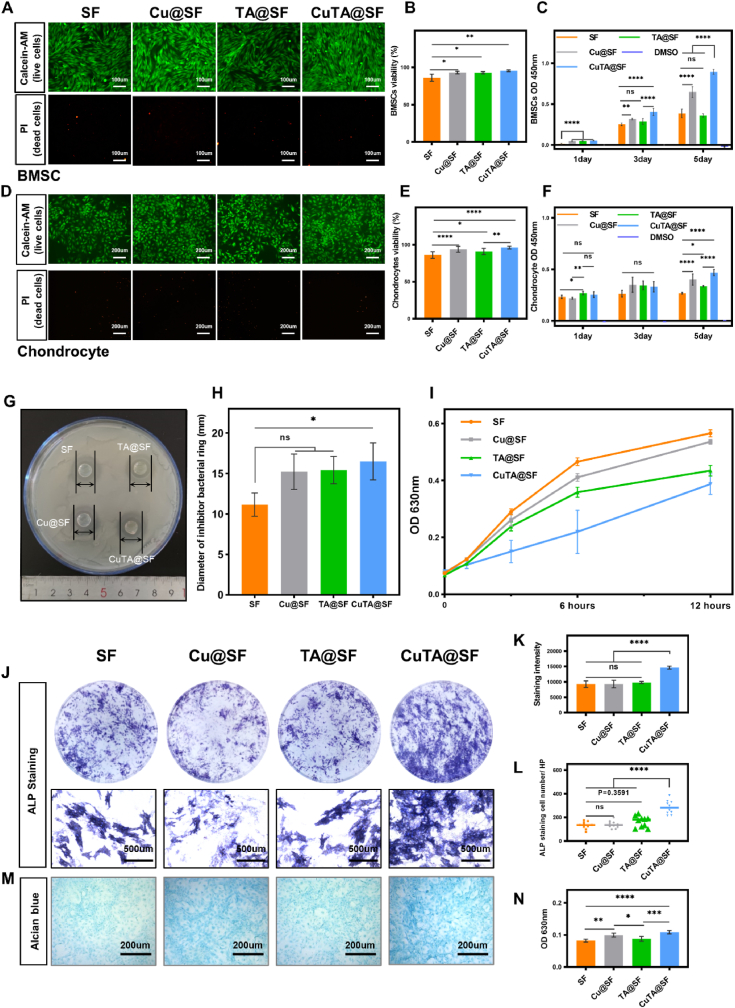
Fig. 3.
(A) Cell viability of BMSCs cultured in the extract of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels was evaluated with Live/dead staining. (B) Quantification of BMSCs viability with the image of Live/dead staining. (C) The proliferation of BMSCs cultured in the extract of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels at 1,3,5 days was evaluated with CCK-8. (D) Cell viability of chondrocytes cultured in the extract of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels was evaluated with Live/dead staining. (E) Quantification of chondrocytes viability with the image of Live/dead staining. (F) The proliferation of chondrocytes cultured in the extract of SF, Cu@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels at 1,3,5 days was evaluated with CCK-8. (G) The image of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels were placed on the agar medium containing Staphylococcus aureus. (H) The anti-bactericidal activity of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels were evaluated with the inhibition halo diameters against Staphylococcus aureus. (I) The antibacterial activity of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogel was evaluated by microplate proliferation assay. (J) Stereoscope and microscopic images of BMSCs co-stained with ALP and DAPI. (K) Quantification of ALP staining with stereoscope images. (L) The number of ALP positive-stained cells. (M) Alcian blue staining for chondrocytes cultured in the extract of SF, Cu@SF, TA@SF and CuTA@SF hydrogels. (N) Quantification of Alcian blue staining. Results were shown as mean ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.