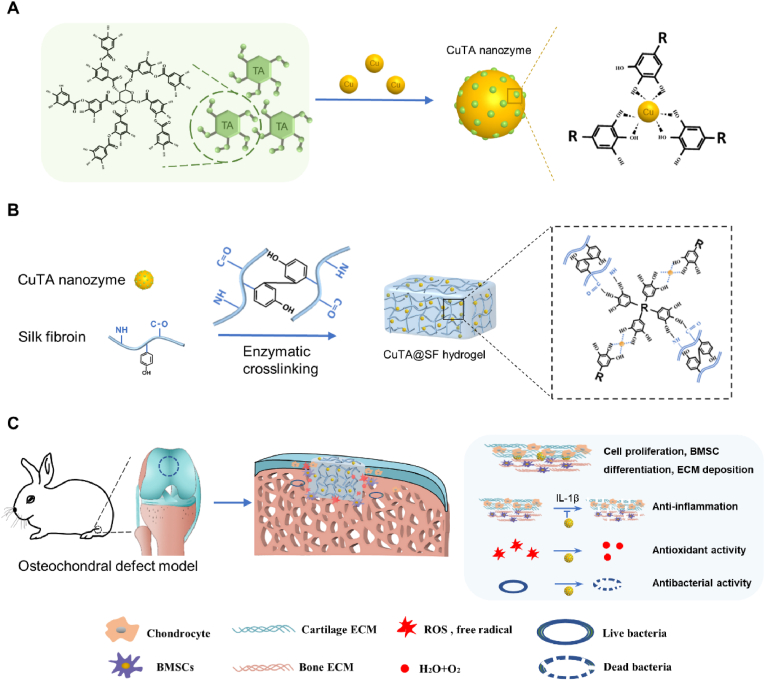
Scheme 1.
(A) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of CuTA nanozyme. (B) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of enzymatically crosslinked CuTA@SF hydrogel and the reasonable form of intermolecular connection inside CuTA@SF hydrogel. (C) In the osteochondral defect model of rabbits, the implantation of CuTA@SF hydrogel promoted cell proliferation, BMSC differentiation and ECM deposition. Moreover, CuTA@SF hydrogel had antioxidant, anti-inflammation and antibacterial capacities.