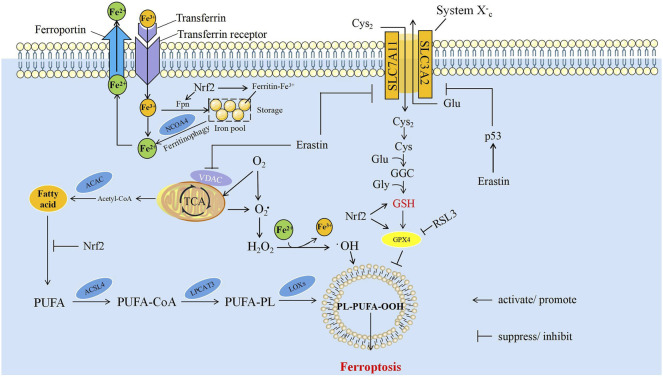
FIGURE 1.
The mechanism of ferroptosis. The core mechanisms affecting ferroptosis are mainly iron metabolism, lipid peroxidation and amino acid metabolism. ACAC, acetyl CoA carboxylase; ACSL4, acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain member 4; Cys, cysteine; Cys2, cystine; Fe2+, ferrous ion; Fe3+, ferric ion; Fpn, ferroportin; Glu, glutamate; Gly, glycine; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GSH, glutathione; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyl-transferase 3; LOXs, lipoxygenases; NCOA4, nuclear receptor coactivator 4; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; O2, oxygen; O2, Oxygen free radicals, PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acids; PUFA-CoA, polyunsaturated fatty acids-CoA; PUFA-PL, polyunsaturated fatty acids-phospholipids; PL-PUFA-OOH, phospholipids-polyunsaturated fatty acids-peroxide; SLC3A2, solute carrier family 3 member 2; SLC7A11, solute carrier family 7 member 11; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle.