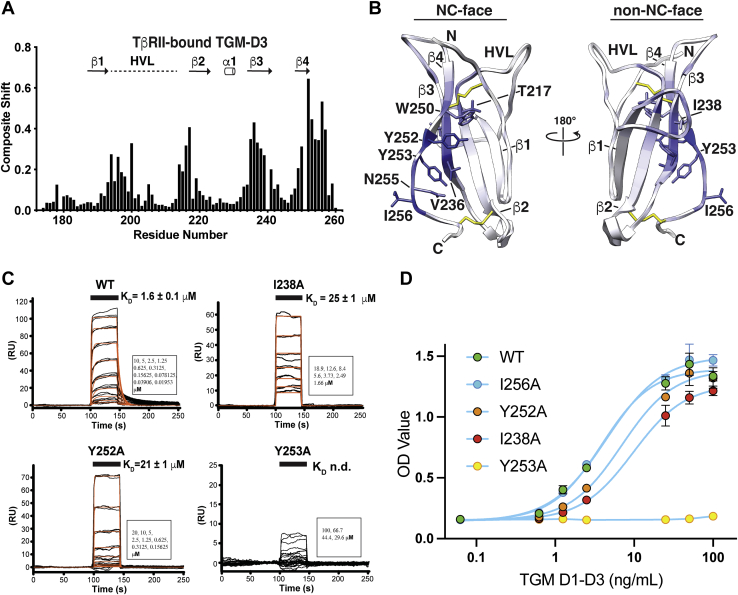
Figure 7.
Binding of TβRII to TGM-D3.A and B, composite shift perturbations of TGM-D3 upon binding to TβRII (A) and a depiction of these on the structure of TβRII (B). Secondary structure shown above the composite shifts in A corresponds to the secondary structure as deduced from the TGM-D3 solution structure. Structure in B is colored using a scale where white indicates minimal composite shift perturbation and dark blue indicates maximal shift perturbation. C, binding of TβRII by TGM-D3 variants as assessed by SPR. SPR sensorgrams obtained upon injection of WT, I238A, Y252A, or Y253A TGM-D3 over immobilized TβRII. Sensorgrams, obtained upon injection of a 2-fold dilution series of each TGM construct, are shown in black, with the fitted curves in orange (data for Y253A were not fit due to weak signal). Black bars shown above the sensorgrams specify the injection period. Injected concentrations are shown in the lower right. D, impact of TGM-D3 mutations on TGF-β signaling as measured through the MFB-F11 TGF-β responsive bioassay. I256A (blue), Y252A (orange), I238A (red), and Y253A (yellow) were assessed for TGF-β signaling and compared to WT TGM1-D13 (green). SPR, surface plasmon resonance.