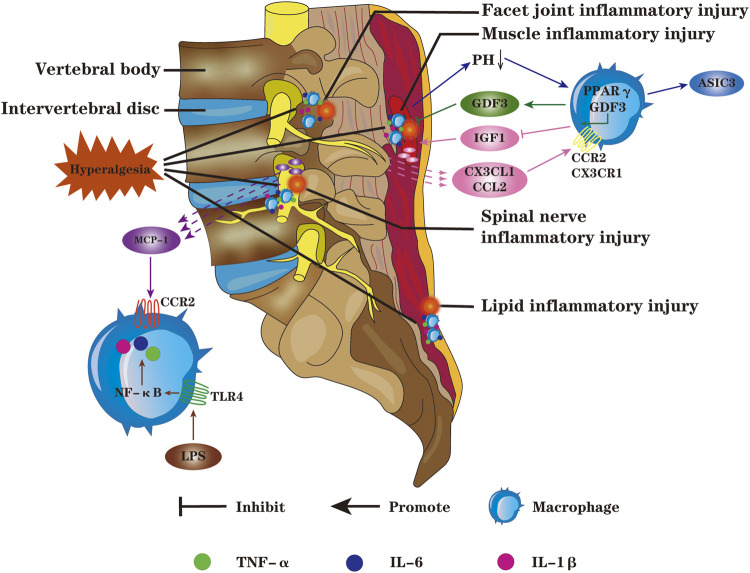
FIGURE 3.
Macrophages can chemotaxis and migrate to adjacent tissues of IVD such as paraspinal muscles, DRG, facet joints and fat; and then synthesize more pro-inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, resulting in spinal cord hyperalgesia, inducing or exacerbating LBP. The macrophages toward M1 polarization will lead to the accumulation of lactic acid in muscle, and the decrease of PH value can up-regulate the expression of ASIC3. Macrophages infiltrating into the damaged DRG promote the secretion of inflammatory mediators and induce neurogenic pain; macrophages can infiltrate the facet joints, aggravate the inflammation and degeneration of the facet joints, and cause LBP. Macrophages are the main source of GDF3 in damaged tissues, and PPARY in macrophages can promote tissue repair and regeneration by regulating the expression of GDF3. Chemokines CX3CL1 and CCL2 recruit macrophages and bind to CX3CR1 and CCR on macrophages,respectively, inhibiting the release of IGF1 and aggravating the inflammatory response; the chemokine MCP-1 could bind to CCR2, inducing and aggravating inflammation. The LPS acting on TLR4 in macrophages will lead to increased release of pro-inflammatory factors through the NF-KB signaling pathway.