FIGURE 3.
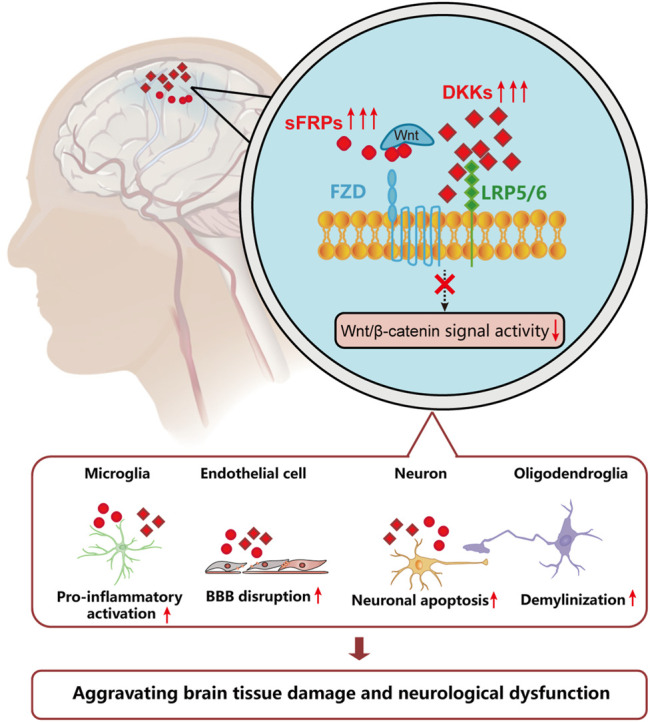
The potential implications of Wnt/β-catenin among cells from ischemic brain. After an ischemia incident, the microenvironment in ischemic brain leads to decreased activity of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The regulatory mechanisms of which include increased level of Dkks and sFRPs, which leads to increased BBB disruption, neuronal apoptosis, demyelination, and overactivation of microglia.
