Figure 4.
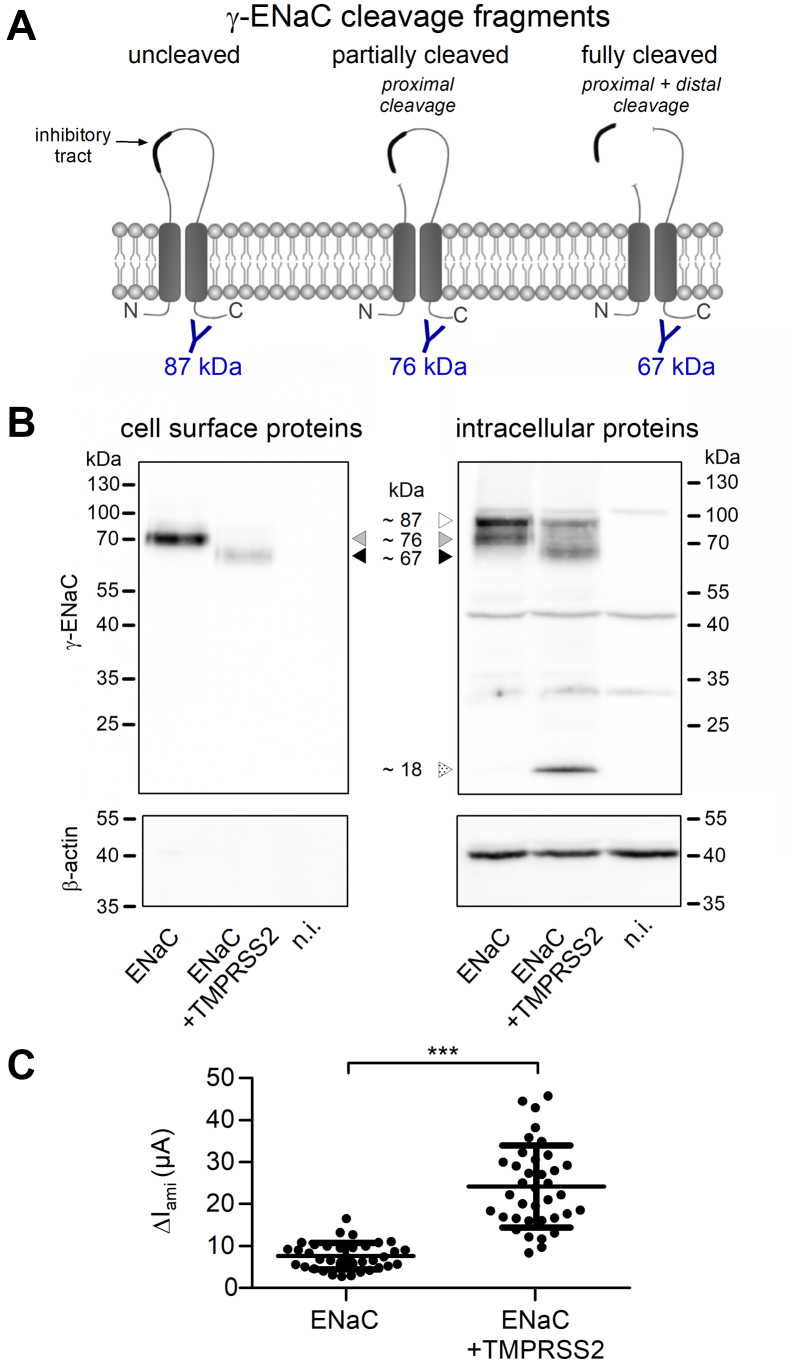
TMPRSS2-dependent ENaC stimulation was associated with the appearance of fully cleaved γ-ENaC in the intracellular and cell surface protein fraction.A, schematic diagram showing γ-ENaC cleavage fragments, which can be detected using an antibody (in blue) raised against a C-terminal γ-ENaC epitope. The expected molecular weights of the corresponding C-terminal γ-ENaC cleavage fragments are given below. B, representative western blots showing cell surface (left upper panel) or intracellular (right upper panel) expression of γ-ENaC in oocytes from one batch expressing ENaC alone or coexpressing ENaC with TMPRSS2. Specific signal of γ-ENaC was detected using an antibody against the C-terminal epitope of γ-ENaC. To increase ENaC expression and improve γ-ENaC detection in western blot experiments, oocytes were injected with more than the usual amount of cRNA for ENaC (1 ng/subunit/oocyte) and TMPRSS2 (5 ng/oocyte). Noninjected oocytes served as a control (n.i.). Uncleaved (∼87 kDa), partially cleaved (∼76 kDa), and fully cleaved γ-ENaC (∼67 kDa) are indicated by open, gray, and black-filled arrowheads, respectively. A putative γ-ENaC degradation product (∼18 kDa) is indicated by an open arrowhead with dot pattern. To validate separation of cell surface proteins from intracellular proteins, blots were stripped and reprobed using an antibody against β-actin (lower panels). Similar results were obtained in four additional repeats (n = 5). C, in parallel experiments to those shown in (B), ΔIami values were measured to confirm the stimulatory effect of TMPRSS2 on ENaC in these batches of oocytes (n = 37, N = 5). Note that the relative stimulatory effect of TMPRSS2 on ΔIami was similar to that for Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, but the absolute current values were higher, which reflects increased ENaC expression because of the larger amount of cRNA injected in these experiments. Mean ± SD and data points for individual oocytes are shown; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. cRNA, complementary RNA; ENaC, epithelial sodium channel; TMPRSS2, transmembrane serine protease 2.