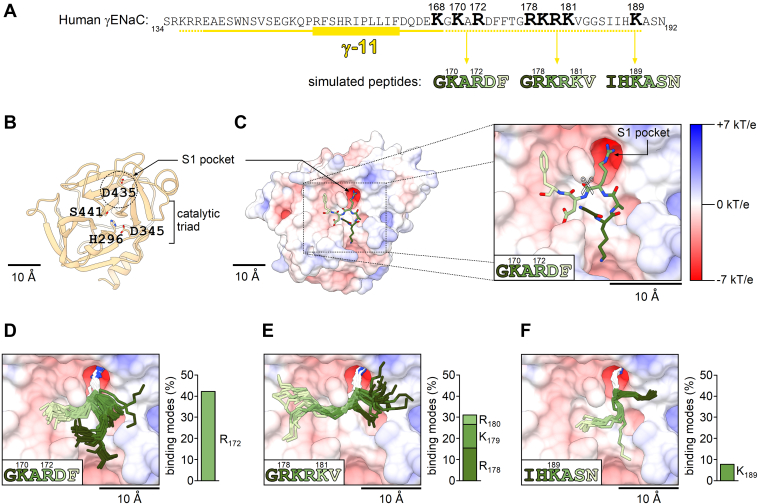
Figure 6.
Prediction of putative TMPRSS2 cleavage sites distal to the γ-inhibitory tract using a molecular docking approach.A, the primary sequence of human γ-ENaC (amino acid residues 134–192) is shown in the region including the γ-inhibitory tract (underlined in yellow). The key inhibitory amino acid sequence (γ-11) is highlighted with a yellow rectangle. Candidate TMPRSS2 cleavage sites (arginine and lysine residues) distal to the γ-inhibitory tract are in bold and numbered. The length of the amino acid sequence released by cleavage may slightly vary depending on the cleavage site used in the region indicated by the dashed yellow line. Sequences of three 6-mer peptides, which were docked to the catalytic domain of TMPRSS2 in computer simulations, are shown below the γ-ENaC sequence. The numbering of amino acid residues in the simulated peptides is the same as in the γ-ENaC sequence. B and C, a homology model of human TMPRSS2 generated based on the crystal structure of human homologous protease hepsin (PDB accession no.: 1Z8G) is shown in ribbon (B) or electrostatic potential molecular surface representation (C). In (B), amino acid residues forming the catalytic triad (histidine H296, aspartate D345, and serine S441) and the aspartate residue D435 at the bottom of the S1 pocket are shown in stick representation with carbons in tan, nitrogens in blue, and oxygens in red. In (C), a representative binding mode of the GKARDF-peptide to the TMPRSS2 catalytic domain (in the inset on an expanded scale), which fulfills the selection criteria described in Figure S2A, is depicted in stick representation with carbons in the same color as the corresponding amino acid residue of the peptide sequence given in the lower left corner of the inset, nitrogens in blue, and oxygens in red. Hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity. Scissile peptide bond is marked in the inset with a scissors symbol (✄). D–F, all binding modes that fulfill the selection criteria are shown for the GKARDF-peptide (D), GRKRKV-peptide (E), or IHKASN-peptide (F). Peptide backbone carbons and nitrogens (in the same color as the corresponding amino acid residue of the peptide sequence given in the lower left corner) and the side chains of arginine or lysine residues occupying the S1 pocket (with carbons in white and nitrogens in blue) are shown. Bar diagrams demonstrate the percentage of binding modes, which fulfill the selection criteria out of the total number of binding modes (90) generated for each peptide, and indicate the arginine or lysine residue that occupies the S1 pocket. ENaC, epithelial sodium channel; PDB, Protein Data Bank; TMPRSS2, transmembrane serine protease 2.