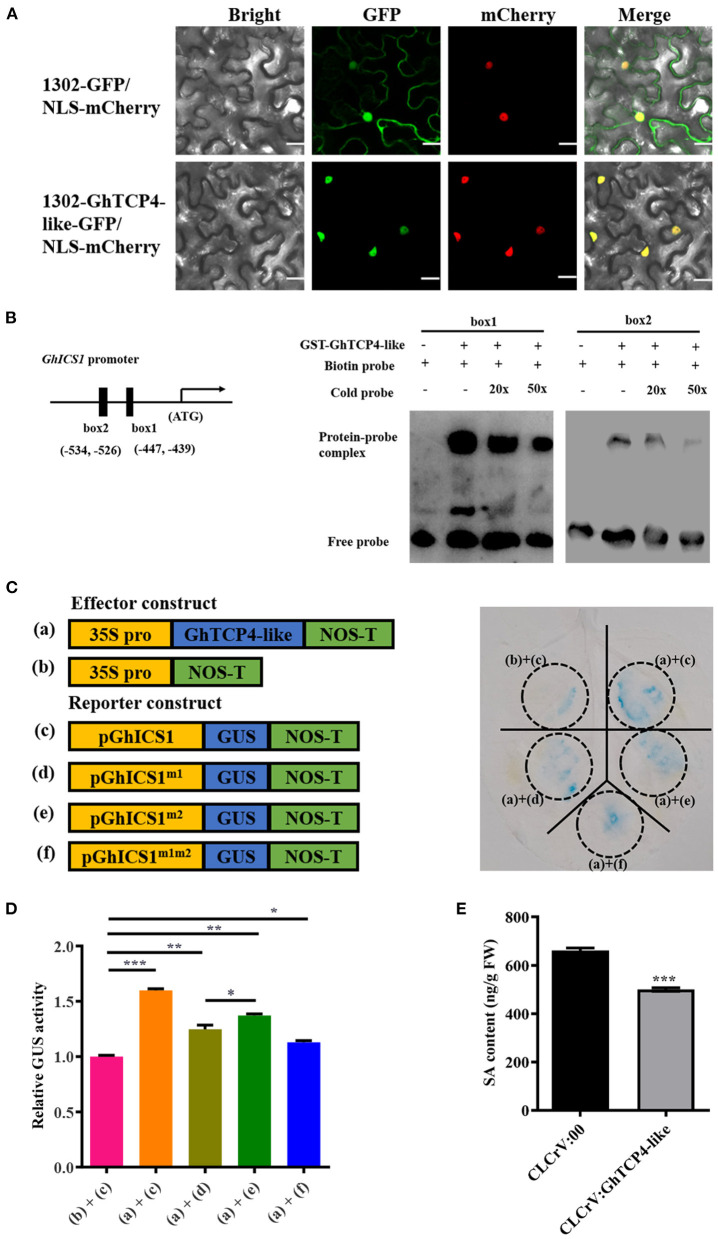
Figure 5.
GhTCP4-like directly transactivates GhICS1 expression. (A) Subcellular localization of GhTCP4-like in tobacco leaf cells. NLS-mCherry was a nuclear location marker. Scale bar = 20 μm. (B) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). Structure of GhICS1 promoter in the left panel. Solid black boxes indicate predicted two GhTCP4-like binding sites (GTGGCACC) in the GhICS1 promoter. GhTCP4-like bound to GTGGCACC motif from GhICS1 promoter in the right panel. The lower bands represent unbound probes; lagging bands indicate the complexity of protein and probe. (C) GUS reporter analysis for GhTCP4-like transactivating GhICS1 expression. Schematic diagram of the constructs for GUS reporter assays in tobacco leaf cells in the left panel. (a), (b), (c), (d), (e), and (f) represent p35S:GhTCP4-like, pCAMBIA1300, pGhICS1:GUS, pGhICS1m1:GUS, pGhICS1m2:GUS and pGhICS1m1m2:GUS, respectively. Tobacco leaves were harvested at 48 h after agroinfiltration. (D) GUS enzyme activity assayed by 4-MU measurement of treated leaf spots indicated in (C). “+” indicates that the corresponding treatment has been added, “–“ indicates that the corresponding treatment has not been added. Tobacco leaves were harvested at 48 h after agroinfiltration. (E) Determination of total SA content. SA of GhTCP4-like-silenced and control plants 1 d after V. dahliae infection was measured by HPLC-MS/MS. Error bar means SD of three independent biological replications. Student's t-test was performed, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. All experiments were repeated more than three times with similar results.