FIGURE 4. Heat inactivation during cDNA synthesis completely inactivates SARS-CoV-2 in scRNA-seq emulsions.
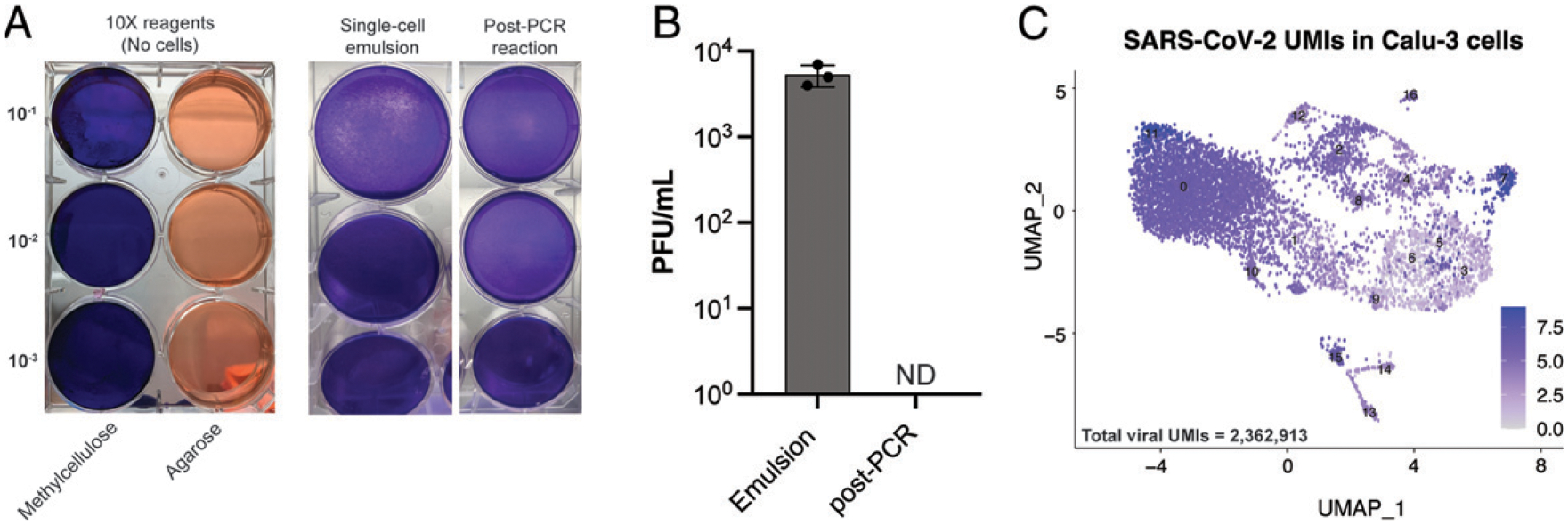
(A) Representative plaque assays performed using 10x Genomics emulsion reagents alone (without cells) to evaluate reagent cytotoxicity on Vero E6 cells and single-cell emulsion with SCV2-WA1–infected Vero E6 cells (MOI of 0.04), and the same emulsion after cDNA synthesis PCR reaction (45 min at 53°C followed by 5 min at 85°C). Duplicate samples were evaluated in two independent experiments. (B) Quantification of viral load in single-cell emulsions of SCV2-WA1–infected Calu-3 cells (MOI of 0.04) immediately after encapsulation and following PCR reaction for cDNA synthesis. n = 3 independent samples reported as averaged duplicates from a single experiment. ND, not detected (by plaque assay). (C) Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) visualization of scRNA-seq data from SCV2-WA1–infected Calu-3 cells (MOI of 0.04; n = 8061 cells) showing expression of the 12 SARS-CoV-2 genes and total viral UMIs (inset).
