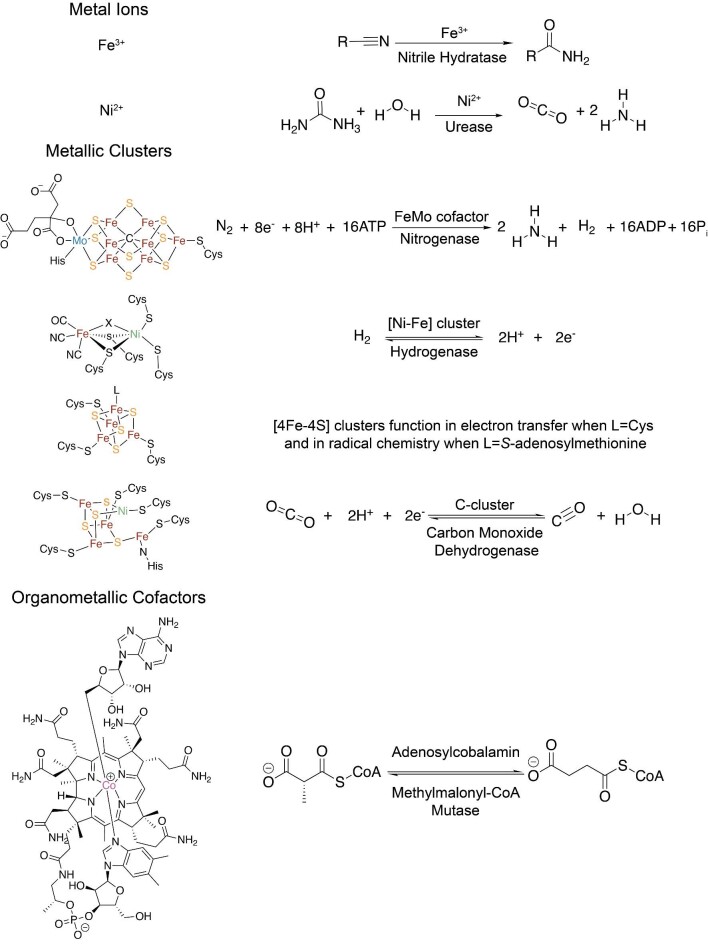
Fig. 1.
Metallocofactors vary widely in structure and reactivity. In some reactions, metal ions such as Fe3+ or Ni2+ are ligated by residues of the metalloprotein but still require metallochaperones for proper maturation. Increasingly complex metallic clusters, such as the FeMo-cofactor and [4Fe–4S] clusters, are transported and inserted by metallochaperones, whereas other metallic clusters, such as the [NiFe] cluster, are assembled in situ. Additionally, organometallic cofactors are often metabolically expensive and are transported by metallochaperones into their target metalloenzyme to perform difficult chemistry.