Fig. 2.
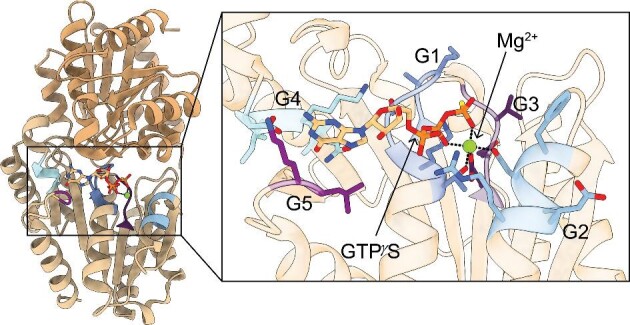
Dimeric structure of P-loop-containing G3E GTPase metallochaperone with conserved motifs. (Left) Representative structure: HypB from Methanocaldococcus jannaschii (PDB 2HF8) with guanosine 5′-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) (GTPγS) and Mg2+ bound.37 Structure is a dimer with each monomer containing a G-domain. (Insert) The GTP-binding site contains the G1–G5 motifs, which are highlighted. The G1 residues (dark blue), also known as the Walker A motif, interact with the α and β phosphates and the bound Mg2+ ion. The G2 residues (light blue), also known as switch I, change conformation based on the nucleotide state and the conserved aspartate residue coordinates the bound Mg2+ ion. The G3 residues (dark purple), also known as the Walker B motif, coordinate the γ-phosphate and the bound Mg2+ ion. The G4 residues (cyan) confer nucleotide specificity as they interact with the base of the nucleotide. The G5 residues (light purple) are involved in nucleotide dissociation.
