FIGURE 7.
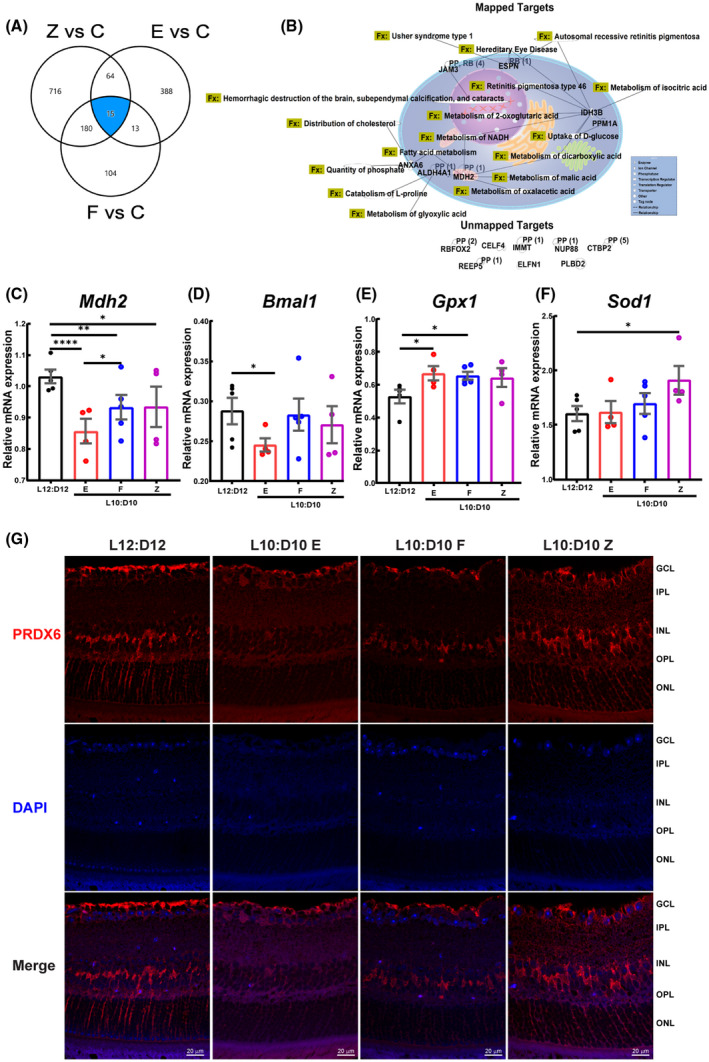
Comparative analysis of retinal proteome and Prdx6 expression in retinal sections. A comparison analysis was performed using IPA (A) Venn diagram showing common dysregulated proteins shared by different behaviors. (B) The protein targets common to these three behaviors were mapped to show their connectivity and function (Fx) and PP‐protein‐protein interactions. RB‐regulation of binding, RBFOX2‐RNA binding fox‐1 homolog 2, ELFN1‐extracellular leucine‐rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 1, JAM3‐junctional adhesion molecule 3, NUPP88‐ nucleoporin 88, CTBP2‐c‐terminal binding protein 2, PLBD2‐ phospholipase B domain containing 2, CELF4‐ CUGBP elav‐like family member 4, REEP5‐receptor accessory protein 5, IMMT‐inner membrane mitochondrial protein. Target validation using qRT‐PCR showing mRNA expression of (C) Mdh2 (D) Bmal (ARNTL), (E) Gpx, and (F) Sod1. mRNA expression was determined in triplicate for each mouse and represented as an average data point for each animal. The raw data were analyzed by Linear Mixed Models EM Means followed by a comparison of individual groups with Least Square design (LSD), *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ****p ≤ 0.0001. (G) Retinal sections were immunostained for peroxiredoxin 6 (PRDX6), representative photomicrographs showing the staining for Prdx6 in the cells of INL, putative Müller cell end feet, and nerve fiber layer
