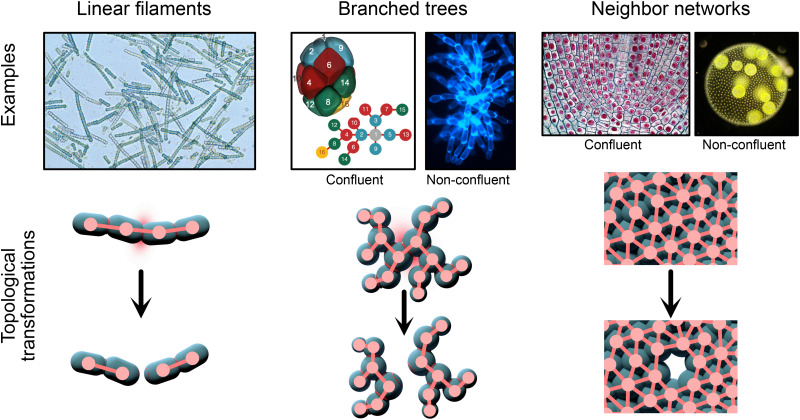
FIG. 3.
Multicellular groups are formed with linear filament and branched tree bond topologies' fragment into two pieces when any one bond is broken. Neighbor-network topologies do not share this property: multiple bonds must be removed to extract any piece of the organism. Experimental images shown left to right are as follows: (i) linear filaments of the cyanobacteria Cylindrospermum sp. courtesy of CSIRO; (ii) membrane-based 3D volume from confocal microscopy of a Drosophila melanogaster embryo, courtesy of Dr. Jasmin Alsous, Flatiron Institute; (iii) branching “snowflakes” of the yeast S. cerevisiae, adapted from Bozdag et al., bioRxiv: 2021.08.03.454982 (2021). Copyright 2021 Author(s), licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) License; (iv) the apical meristem in an onion root tip; (v) the entire green algae organism V. carteri, adapted from Day et al., eLife 11, e72707 (2022). Copyright 2022 Author(s), licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) License.