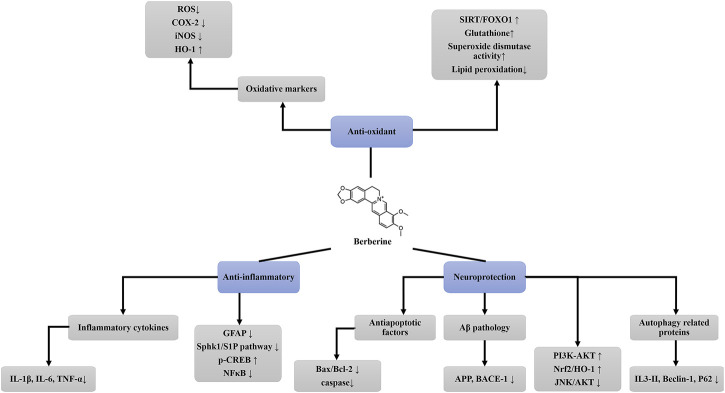
FIGURE 1.
The pharmacological effects of berberine. This schematic drawing shows the anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of berberine and its related molecular mechanisms. ROS, reactive oxygen species; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; iNOS, initric oxide synthase; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; SIRT1, sirtuin1; FOXO1, forkhead box O1; IL-1β, interleukin 1β; IL-6, interleukin 6; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; SphK1, sphingosine kinase-1; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; p-CREB, phosphorylated cAMP response element binding protein; NF-κb, nuclear transcription factor kappa B; Aβ, amyloid β; APP, amyloid precursor protein; BACE1, beta-secretase 1; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT, kinase-protein kinase B; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor-2; JNK, jun amino-terminal kinases.