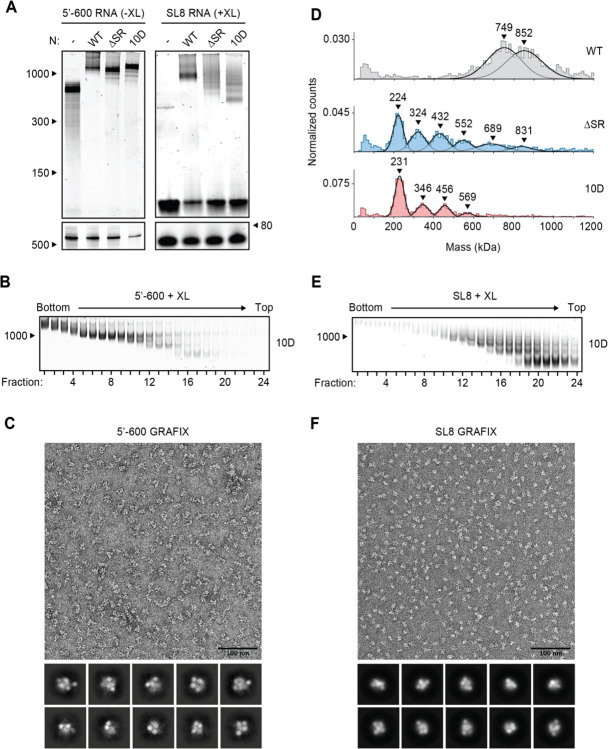
Figure 4. Phosphomimetic mutations in the SR region of N prevent vRNP assembly.
(A) 15 μM N protein constructs were combined with 256 ng/μl 5’−600 RNA (left) or 256 ng/μl SL8 RNA (right) and analyzed by native (top) and denaturing (bottom) gel electrophoresis. SL8 ribonucleoprotein complexes were crosslinked prior to native gel electrophoresis. WT, wild type. See Fig. 5A for the ten sites of phosphorylation mutated to aspartic acid in the 10D mutant. (B) 15 μM phosphomimetic N protein (10D) was mixed with 256 ng/μl 5’−600 RNA and separated by glycerol gradient centrifugation in the presence of crosslinker (GraFix). Fractions were collected and analyzed by native gel electrophoresis. (C) Fractions 7 and 8 of GraFix-separated vRNPs (from B) were combined and analyzed by negative stain electron microscopy and two-dimensional classification. (D) 15 μM N protein mutants were mixed with 256 ng/μl SL8 RNA, crosslinked, and analyzed by mass photometry. Representative of at least two independent experiments (table S1). A separate analysis of ΔSR mutant is also shown in Fig. 3D. (E) 15 μM 10D N protein was mixed with 256 ng/μl SL8 RNA and separated by GraFix. Fractions were analyzed by native gel electrophoresis. (F) Fractions 19 and 20 of GraFix-purified 10D N in complex with SL8 RNA (from E) were combined and visualized by negative stain electron microscopy and two-dimensional classification.