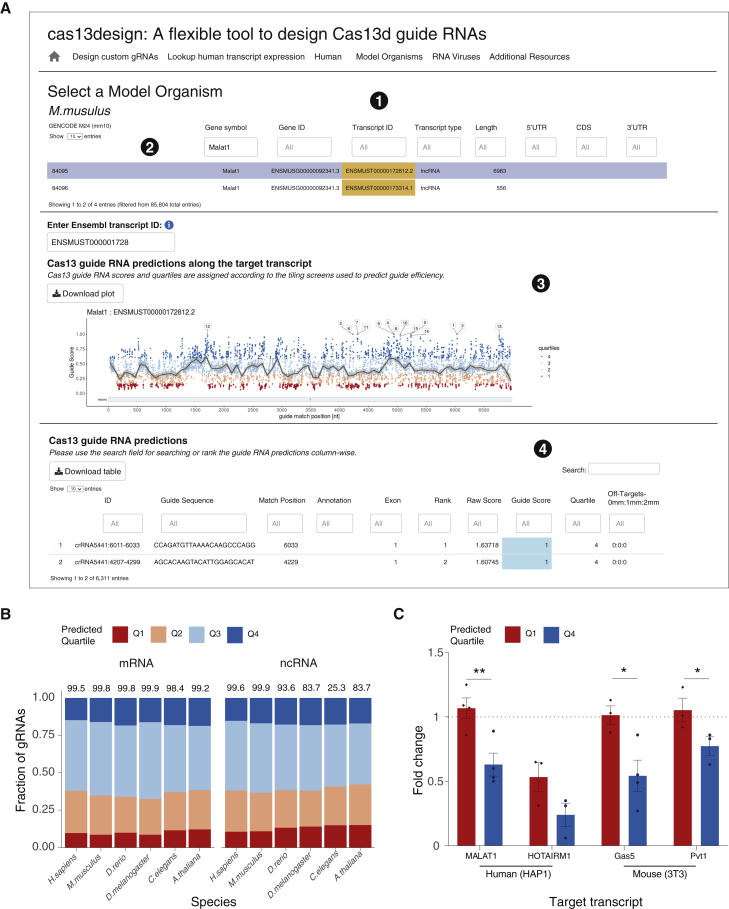
Figure 1.
A graphical interface for optimized CRISPR-Cas13d gRNA design for messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) from six common model organisms
(A) Example output of the cas13design webtool. (1) Selection of model organisms. (2) Searches by gene symbol or transcript ID for gRNA design, with options to download generated plots and data tables. (3) Interactive display of gRNAs along the target transcript, color coded by the predicted targeting efficacy scores separated into four quartiles. Q4 gRNAs correspond to those with the highest predicted efficacy, and Q1 gRNAs correspond to those with the lowest predicted efficacy. (4) Display of gRNA options with on-target score predictions and potential off-targets by number of mismatches (number of sequences in the transcriptome with 0, 1, or 2 mismatches).
(B) The predicted guide efficacy quartiles for mRNAs and ncRNAs across six model organisms. The percentage of scored transcripts that meet the minimal length requirement for target RNAs (80 nt) is indicated above each bar.
(C) Average lncRNA knockdown for Q4 and Q1 gRNAs (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, two-tailed Student’s t test; mean ± SEM, n = 3–4 different gRNAs from the specified prediction quartile, each transduced with three biological replicates).
See also Figure S3.