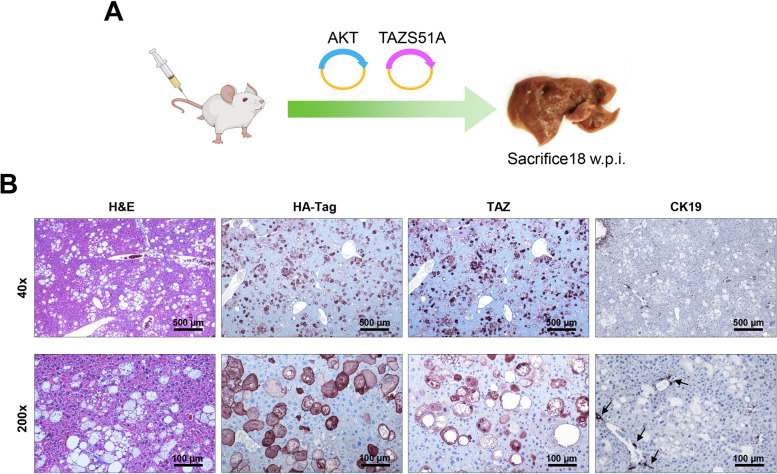
Fig. 7.
Taz oncogenic activity depends on its functional interaction with TEAD factors in AKT/TAZ mice. (A) Scheme of the experiments conducted. (B) Blockade of TAZ binding to TEAD transcription factors by hydrodynamic transfection of the TAZS89AS51A plasmid (TAZS51A) inhibits AKT/TAZ-dependent cholangiocarcinogenesis in the mouse liver. At the histological levels, the livers of AKT/TAZ mice are indistinguishable from those of mice injected only with Myr-AKT, consisting of clusters of lipid-rich giant cells. As expected, the transfected cells show positive immunoreactivity for HA-Tag(AKT) and nuclear TAZ. Due to the disappearance of cholangiocellular lesions, the staining for the biliary marker CK19 is restricted to normal biliary cells. Original magnification: 40x and 200x; scale bar: 500 μm in 40x, 100 μm in 200x. Abbreviations: H&E, hematoxylin and eosin staining.