Figure 3.
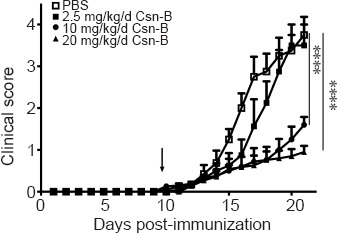
The NR4A1 agonist cytosporone B (Csn-B) can suppress the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis symptoms in vivo.
After induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein peptide 35–55 and pertussis toxin, 2.5, 10, or 20 mg/kg Csn-B or PBS was administered to the mice once per day from day 10 to 21 post-immunization (the arrow represents the time of administration). The clinical function score showed no significant difference between the mice treated with 2.5 mg/kg/d Csn-B and the PBS control group, whereas the clinical function scores for the 10 and 20 mg/kg/d Csn-B groups were significantly lower than the scores for mice treated with PBS. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 5/group). ****P < 0.001 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni post hoc test). Csn-B: cytosporone B; MOG35–55: myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-35–55; PBS: phosphate buffer saline.
