Figure 4.
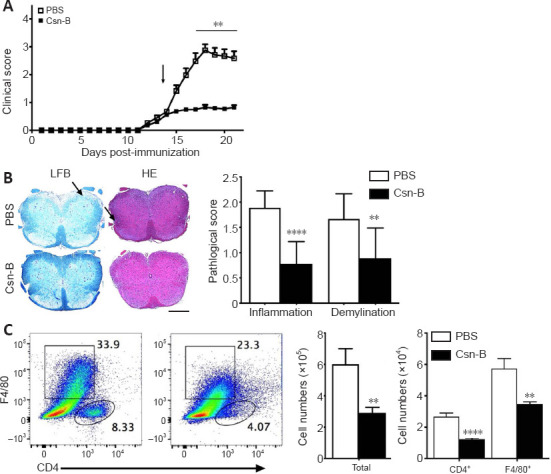
Cytosporone B (Csn-B) attenuates clinical symptoms and reduces demyelination and inflammatory cell infiltration in the central nervous system.
After induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein peptide 35–55 and pertussis toxin, 10 mg/kg Csn-B or PBS was administered to the mice once per day from day 14 to 21 post-immunization. L3 spinal cords were harvested on day 21. (A) Clinical symptom scores. The arrow represents the time of Csn-B or PBS administration. (B) Luxol fast blue (LFB) staining shows demyelination, and hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining shows inflammation (left panel). PBS-treated EAE mice demonstrated more severe demyelination and greater inflammatory cell infiltration (arrows) compared with that observed in the Csn-B-treated EAE mice. The pathological scores for inflammation and demyelination are presented in the bar graphs (right panel). Scale bars: 200 µm. (C) Flow cytometry was used to detect CD4+ T and F4/80+ cells in the central nervous system of PBS-treated (left plot) and Csn-B-treated (right plot) based on the gated populations. The black boxes represent the distribution and percentage of F4/80+ cells, and the oval boxes represent the distribution and percentage of CD4+ cells. Absolute numbers of CD4+ T and F4/80+ cells are presented in the bar graphs (right panel). Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 4 per group). **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.001 (Student’s t-test). Csn-B: Cytosporone B; HE: hematoxylin-eosin; LFB: Luxol fast blue; PBS: phosphate buffer saline.
