Figure 6.
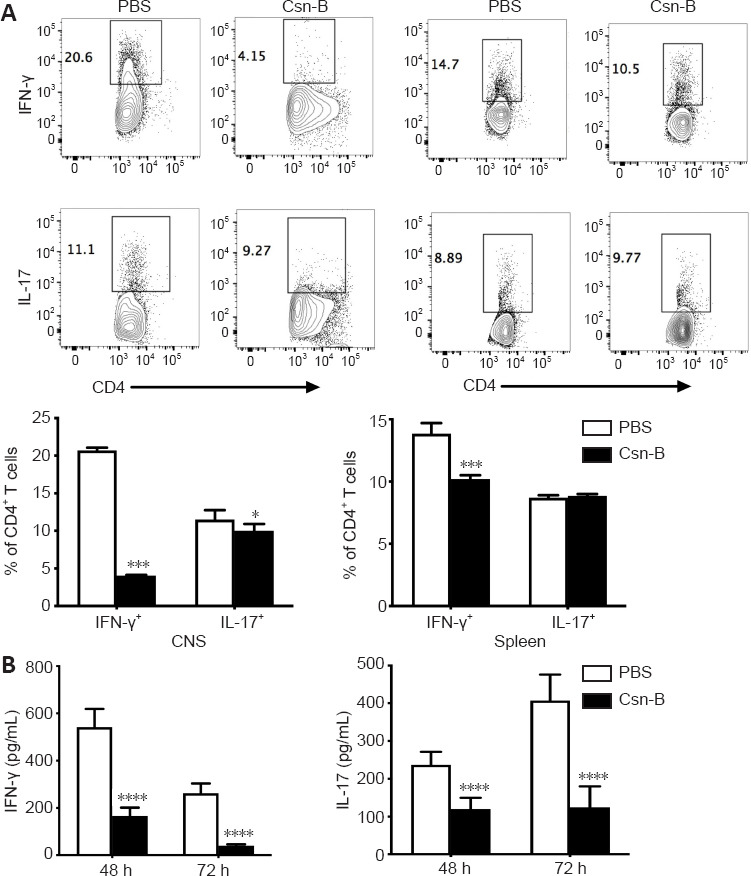
Cytosporone B (Csn-B) decreases T helper (Th)1 and Th17 cell responses in vivo.
After induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, 10 mg/kg Csn-B or PBS was administered once per day from day 14 to 21 post-immunization. The mice were sacrificed on day 21. Infiltrating cells in the central nervous system (CNS) and splenocytes were isolated. (A) Upper: CD4+ T cells were gated within the CNS cell or splenocyte populations and analyzed by flow cytometry. The black boxes represent the distribution and percentages of IFN-γ+ and IL-17+ cells. Lower: Percentages of IFN-γ+ and IL-17+ cells. (B) Splenocytes were cultured in medium containing the myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein peptide 35–55 (25 µg/mL) for 48 and 72 hours. Supernatants were collected and cytokine levels were analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 4 per group). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.005, ****P < 0.001 (Student’s t-test). Csn-B: Cytosporone B; IL-17: interleukin-17; INF-γ: interferon-γ; MOG35–55: myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-35-55; PBS: phosphate buffer saline.
