Figure 5.
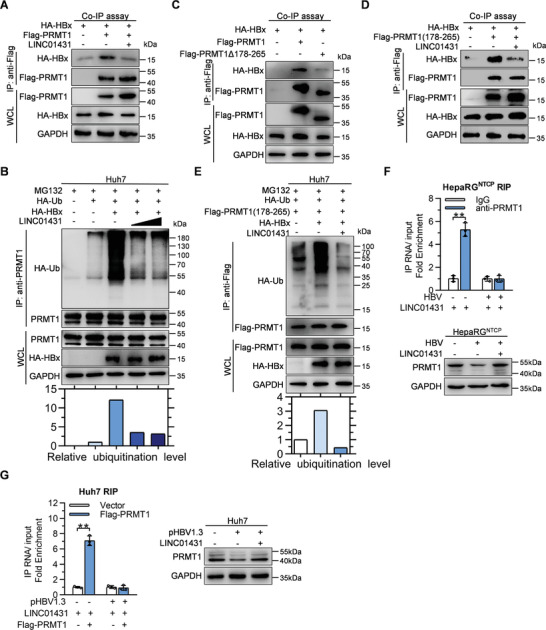
LINC01431 abolishes the HBx‐mediated ubiquitination and degradation of PRMT1. A,C,D) Co‐IP assays evaluating the interaction between PRMT1 and HBx with or without the presence of LINC01431. Huh7 cells were transfected with indicated plasmids, and the CoIP assay was performed at day 3 post transfection using anti‐Flag antibody, followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. B,E) Ubiquitination assay of PRMT1 in Huh7 cells with the presence of MG132, HA‐HBx, and HA‐Ub. The ubiquitination of PRMT1 was detected by immunoprecipitation, followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. F,G) Immunoblot and RIP assay evaluating the interaction of LINC01431 and PRMT1 with or without the presence of HBV. F) HepaRGNTCP cells transfected with LINC01431 were cultured with or without HBV infection, the cells were harvested at 5 dpi and subjected to RIP assay (upper). HepaRGNTCP cells infected with HBV were cultured with or without the presence of LINC01431, the cells were harvested at 5 dpi and subjected to immunoblot (bottom). G) Huh7 cells were transfected with LINC01431 and Flag‐PRMT1 with or without the presence of pHBV1.3, the cells were harvested at day 3 post transfection and subjected to RIP assay (left). Huh7 cells were transfected with pHBV1.3 with or without the presence of LINC01431, the cells were harvested at day 3 post transfection and subjected to immunoblot (right). For immunoblot, MG132 (20 µm) was added before protein extraction to inhibit PRMT1 degradation. RIP was performed with anti‐PRMT1 (F) or anti‐Flag (G) antibody, GAPDH served as the loading control. LINC01431 was amplified by RT‐qPCR and normalized data were shown as relative fold enrichment to the control group. For all experiments, representative of 3 independent experiments. Data information: data were presented as mean ± SD and normalized to the control group. Two‐tail unpaired Student's t‐tests; * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01 (F,G).
