Extended Data Fig 2. The ability of EVs to modulate target cell Klotho and MyoD protein levels is dependent on Klotho mRNAs.
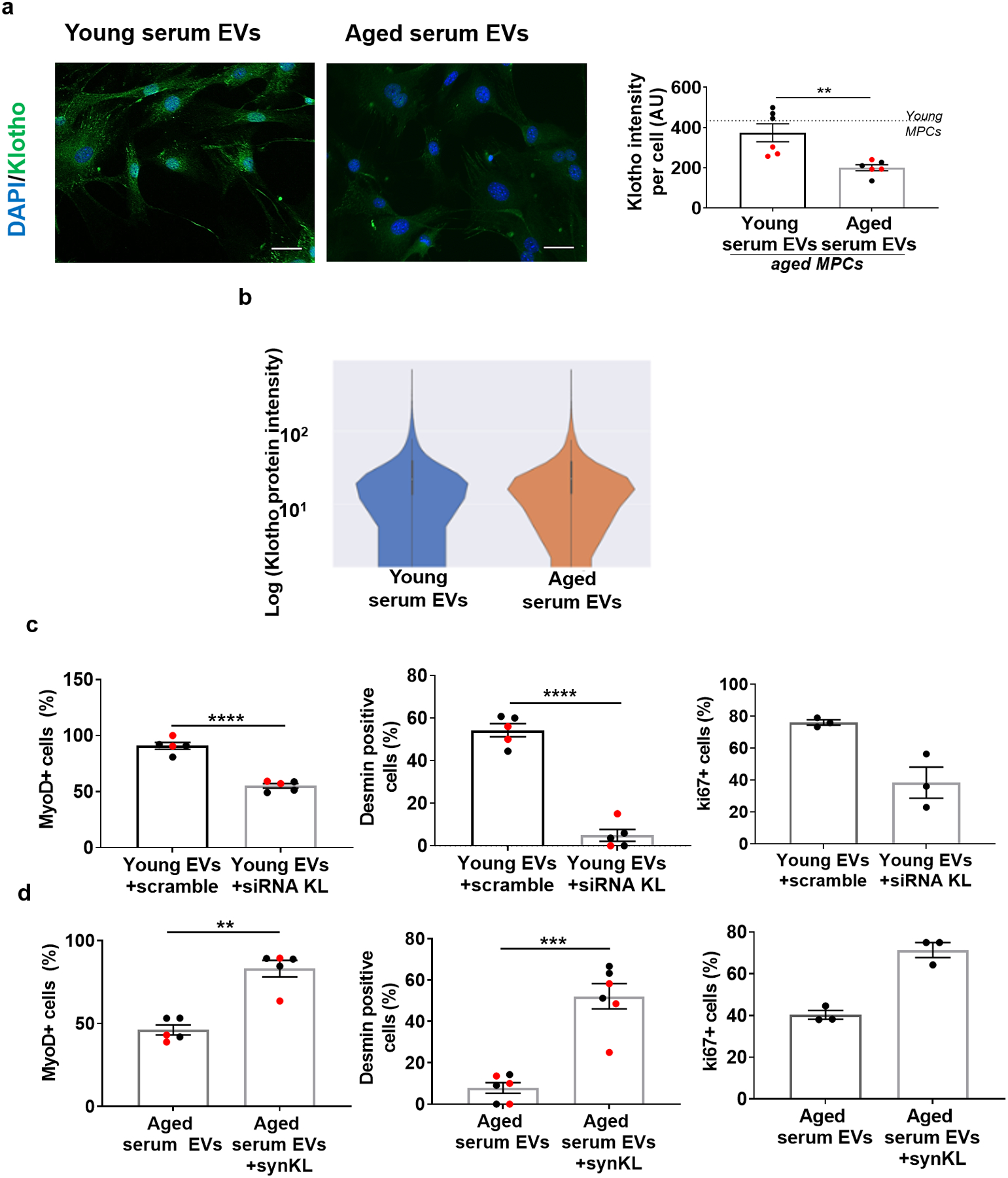
a, Imaging and quantification of Klotho protein in aged MPCs following culture in the presence of young or aged EVs for 24 hours. Scale: 50 μm.(n= 6 wells/group performed over two independent experiments, **p<0.01, two-tailed Welch’s t-test). b, Representative violin plot of Klotho protein intensity per EV from young and aged serum, using imaging flow cytometry. (n=11,229–11,685 EVs/group for this experimental run. EVs pooled from 4 young and 4 aged serum samples, p>0.05, two-tailed Mann Whitney test, experiment repeated in triplicates). Violin plot minima, maxima, median, 25th percentile and 75th percentile are 0, 272915.9, 0, 0, and 26.36 for young, and 0, 272241.3, 0, 0, and 23.2 for aged respectively. c, Quantification of MyoD+ (%), desmin+ (%), and ki67+(%) aged MPCs receiving young serum EVs treated with scramble or siRNA to Klotho or d, aged serum EVs or aged serum EVs loaded with synthetic Klotho mRNA.(MyoD and desmin (scramble, siRNA), desmin (aged EVs, synKL): **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, two-tailed t-test with Welch’s correction, n=5–6 wells/group; MyoD (aged EVs, synKL, **p<0.01, two-tailed Mann Whitney test, n=5 wells/group), ki67 (scramble, siRNA and aged EVs, synKL, p>0.05 (p=0.1), two-tailed Mann Whitney test). Data presented as mean ± SEM. Data from different cohorts or experimental groups performed on different days are presented within the same graph as black or red circles.
