Figure.
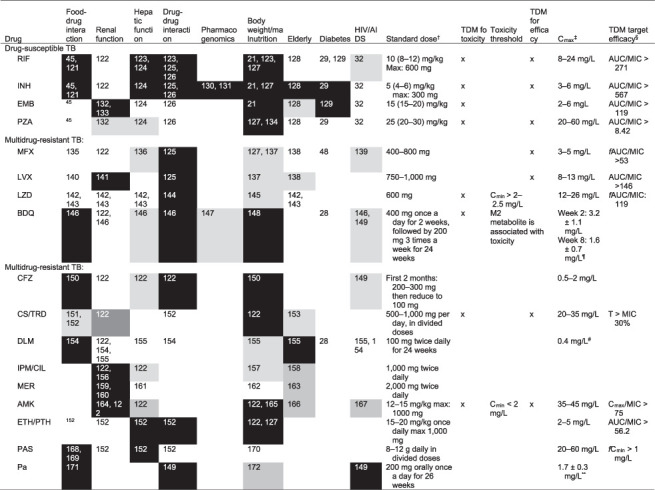
Factors contributing to variability in pharmacokinetics, as well as the efficacy and toxicity of drugs used to treat TB.* *Factors which are likely (black), might (light grey) or are unlikely (white) to contribute to variability in drug efficacy or toxicity and which should be considered when making drug selections or dose adjustments. †WHO-recommended doses for adults.173 ‡Reference values for Cmax after a standard dose.64 §The PK/PD targets were previously reported and are dependent on the precise MIC methodology used in the respective studies.104 Because of the systematic differences between some MIC methods, these targets cannot be used directly with some MIC methods.114 The PK/PD targets should be used in a multiprofessional team experienced in TDM. ¶Reference values for Cmax after standard dose.174 **Reference value for Cmax after standard dose.175 TDM=therapeutic drug monitoring; Cmax=maximum concentration (of a drug); RIF = rifampicin; AUC = area under the curve; INH = isoniazid; EMB= ethambutol; PZA = pyrazinamide; MFX ¼moxifloxacin; LVX = levofloxacin; LZD = linezolid; BDQ = bedaquiline; CFZ = clofazimine; CS = cycloserine; TRD = terizidone; DLM = delamanid; IPM/CIL = imipenem/cilastatin; MER = meropenem; AMK = amikacin; ETH = ethionamide; PTH = prothionamide; PAS = para-aminosalicylic acid; Pa = pretomanid; MIC = minimum inhibitory concentration; fAUC = free area under the concentration time curve; Cmin = minimum concentration (of a drug); PK = pharmacokinetics; PD = pharmacodynamics.
