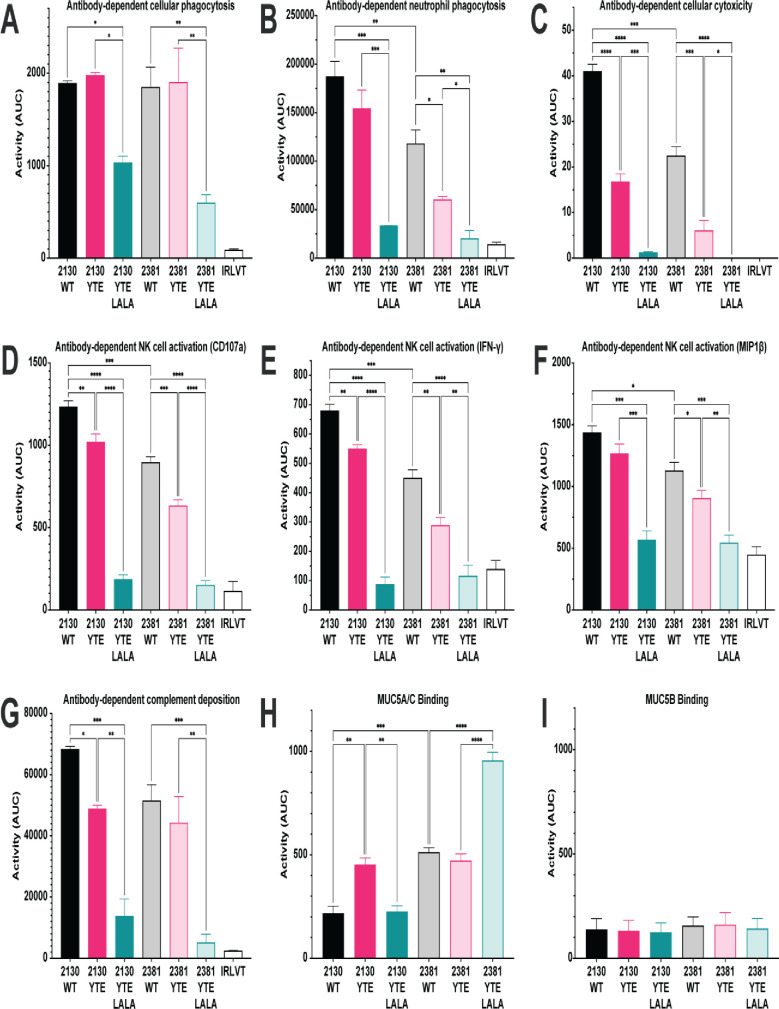
Fig 3. Extra-neutralizing functional activity of the monoclonal antibody variants.
The data are presented both as bar graphs representing the overall activity of the monoclonal antibody variants in the indicated functional assays represented as the area under the curve calculated from the individual dilution curves presented in S2 Fig. Data are presented as the mean AUC ± standard deviation from two independent experiments. For assays using primary cells, cells isolated from two independent donors were used. (A) Antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis; (B) antibody-dependent neutrophil phagocytosis; (C) antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; (D–F) antibody-dependent NK cell activation; (G) antibody-dependent complement deposition; (H) antibody-dependent mucin (MUC5A/C) binding; (I) antibody-dependent mucin (MUC5B) binding. The Ebola virus GP–specific antibody KZ52 was used as the irrelevant antibody. Significance was calculated using a one-way ANOVA with post hoc Holm-Šídák’s multiple comparisons test. *: p ≤ 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.