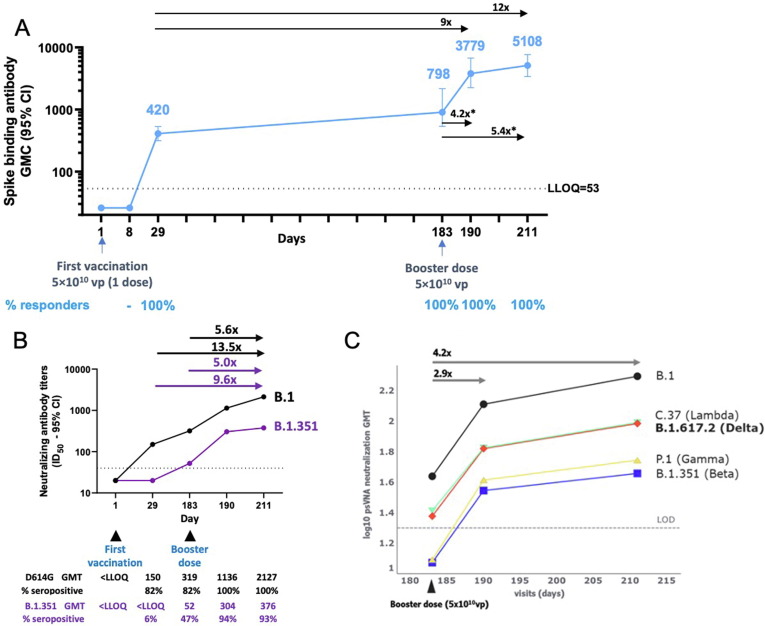
Fig. 4.
Durability of spike-binding antibody responses 6 months after first vaccination and impact of a 6-month booster dose on binding and neutralizing antibodies (phase 1/2a trial). Phase 1/2a participants aged 18–55 years (N = 27) were administered a single dose of Ad26.COV2.S (5 × 1010 vp) at Day 1, and 20 participants received a booster dose of Ad26.COV2.S (5 × 1010 vp) at approximately 6 months (Day 183) after the first vaccination; 17 participants had data available at Day 190. Only participants with booster data available were included in these analyses. (A) Serum spike-binding antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 were evaluated in a validated S-ELISA up to 28 days post-boost (Day 211). Participants aged 18–55 years are represented with a blue line. GMCs are depicted above each time point (error bars represent 95% CIs), and response rates are illustrated at the bottom of the panel. The asterisk denotes geometric mean increase. (B) Serum (N = 17) neutralizing antibody titers were evaluated via validated psVNA against the B.1 (D614G) reference strain and B.1.351 (Beta) variant at Days 1, 29, 183, 190, and 211. Arrows above the graph indicate GMI for Day 211 versus Day 183 and GMR for Day 211 versus Day 29. (C) Serum (N = 17) neutralizing antibody titers against the B.1 (D614G), B.1.617.2 (Delta), C.37 (Lambda), P.1 (Gamma), and Beta variants were evaluated via pre-qualified psVNA at Days 183, 190, and 211. The log10 GMTs per visit per strain were estimated in a Tobit model with subject, visit, strain, and interactions as factors. One participant who was missing data for Day 211 was excluded. With heavy censoring, the estimated GMT is below the LOD. Adjusting for censoring revealed good proportionality. The average GMT fold increase for all variants is indicated above the graph for Days 183–211 and Days 183–190. In all panels, error bars represent 95% CIs. CI, confidence interval; GMC, geometric mean concentration; GMT, geometric mean titer; ID50, serum dilution conferring 50% inhibition; LLOQ, lower limit of quantification; LOD, limit of detection; psVNA, pseudotyped virus neutralization assay; S-ELISA, spike protein enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; vp, viral particles.