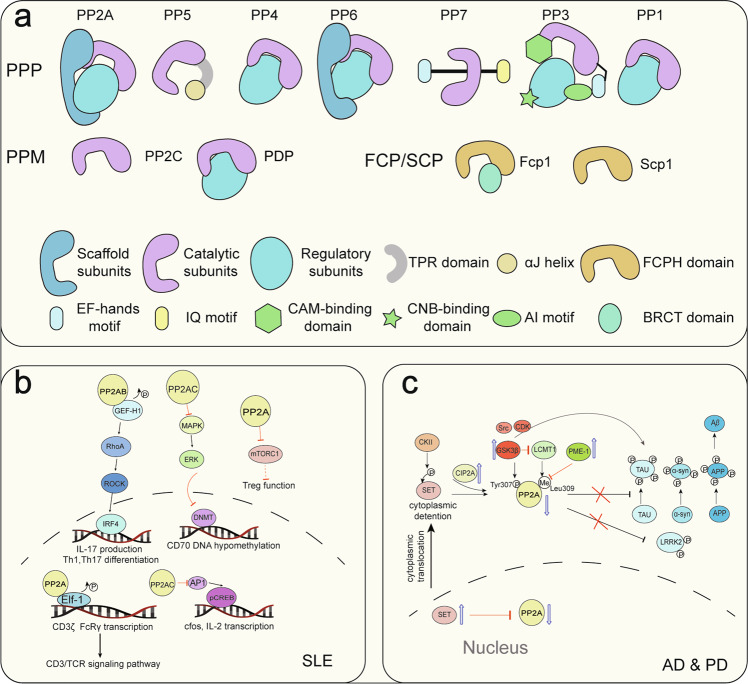
Fig. 3.
The PSP family and the regulated signaling pathways of PP2A in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and Parkinson’s disease (PD). a Representative holoenzymes of 3 PSP families. The PPP family contains 7 subfamilies: PP1, PP2A, PP3, PP4, PP5, PP6, and PP7. The catalytic subunits are conserved. PP5 and PP7 work in monomeric enzyme form, while others work in holoenzyme form with the help of catalytic subunits, regulatory subunits, and/or scaffold subunits. The PPM family contains PP2C and PDP. PP2C works in monomeric enzyme form, and PDP works as heterodimer that consists of a regulatory and a catalytic subunit. FCP/SCPs have a conserved structural core of the FCPH domain. b The role of PP2A and its subunits in regulating immune cell differentiation and activation through major signaling pathways in SLE. The aberrant expression of different subunits of PP2A in SLE results in the activation of CD3 T cells, differentiation of Th1 and Th17 cells, and inhibition of Tregs. c The effects of PP2A on the accumulation of Tau, α-syn, and Aβ protein in AD and PD. In neurodegenerative conditions, nuclear pores start to leak, and SET is translocated to the cytoplasm. It then freely diffuses between the nucleus and cytoplasm, but phosphorylation of SET by CKII (casein kinase II) causes its retention in the cytoplasm. Together with an increased activity of GSK3β in the cytoplasm, the consequence is an increased tau phosphorylation, as indicated. PPP phosphoprotein phosphatases, PDP pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase, FCP TFIIF-associating component of RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase, SCP small CTD phosphatase, APP amyloid-β precursor protein. TPR domain the tetratricopeptide repeat domain, FCPH domain FCP-homology domain, CAM-binding motif calmodulin binding motif, IQ motif calmodulin binding motif in PP7, CNB-binding motif calcineurin B binding motif, AI motif autoinhibitory motif, BRCT domain BRCA1 C-terminal domain like domain