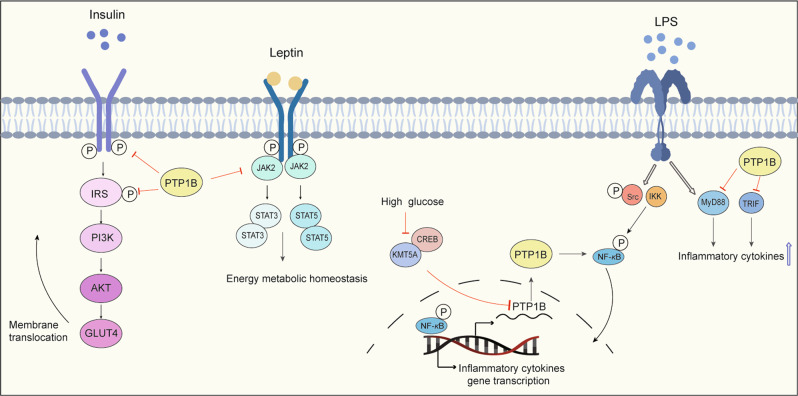
Fig. 8.
The regulated signaling pathways of PTP1B in inflammatory diseases. The role of PTP1B in insulin signaling, leptin signaling, and LPS-TLR-mediated inflammatory signaling in diabetes, obesity, and other inflammatory diseases. PTP1B inhibits the phosphorylation of the insulin receptor and insulin receptor substrate and their downstream PI3K/AKT/GLUT4 signaling, thereby preventing the translocation of GLUT4 to the membrane to transport glucose. PTP1B also inhibits JAK2 phosphorylation and attenuates the leptin JAK2/STAT signaling pathway to affect metabolic energy homeostasis. The CREB/KMT5A complex regulates PTP1B to modulate high glucose-induced endothelial inflammatory factor levels in diabetic nephropathy. PTP1B also acts as a negative regulator of TLR signaling via the suppression of both MyD88- and TRIF-dependent production of proinflammatory cytokines in macrophages stimulated by LPS