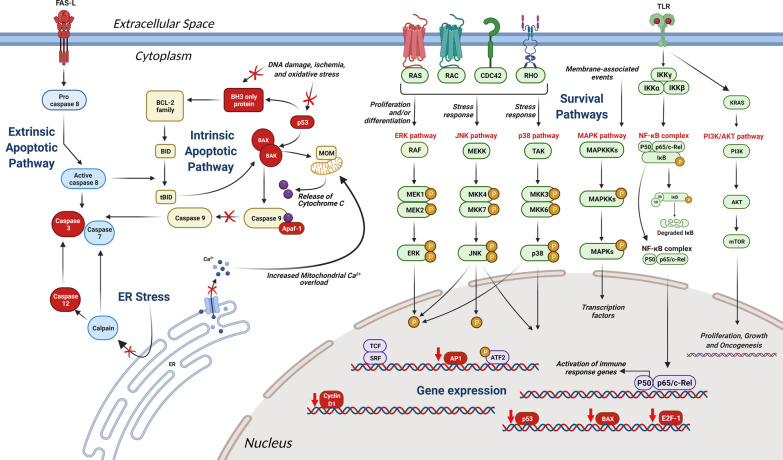
Fig. 2.
Schematic drawing of different possible neuroprotective mechanisms exerted by hydrophilic bile acids, with specific reference to the anti-apoptotic effects of TUDCA on different intracellular pathways. Factors and pathways inhibited by TUDCA are shown in red; pathways blocked by TUDCA are shown by a red cross; genes downregulated by TUDCA are shown by a red downward arrow. Proposed mechanisms of action of TUDCA include: inhibition of the intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, through reduction of ROS and inactivation of BAX, in turn decreasing cytochrome c release; inhibition of the death receptor in the extrinsic apoptotic pathway, with further block of caspase 3; reduction of ER-mediated stress by decreasing caspase 12 activity and Ca2+ efflux decrease from the ER. TUDCA also inhibits the apoptotic induced pathways MAPK, JNK, PI3K, NF-кB, ERK and p38 [27–29]. Furthermore, TUDCA is supposed to reduce the expression of genes involved in cell cycle regulation (Cyclin D1), the Apaf-1 apoptotic pathway, and the E2F/p53/BAX, and AP-1 pathways [30, 31]. Abbreviations: AKT, protein kinase B; AP1, activating Protein-1; Apaf-1, apoptotic protease activating factor-1; ATF2, activating transcription factor 2; BAK, Bcl-2 homologous antagonist killer; BAX, Bcl2-associated X protein; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2 family of regulator proteins; BID, BH3 interacting-domain death agonist C, cytochrome C; CDC42, cell division control protein 42; E2F-1, E2 promoter binding factor 1; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; IKK-α, nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha; IKK-β, nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta; IKK-γ, nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit gamma; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; KRAS, Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene; MAPKs, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MOM, mitochondrial outer membrane; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-ĸB, nuclear factor kappa B; P, phosphate; p53, cellular tumour antigen p53; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinases; RAC, Rho family of GTPases; RAS, rat Sarcoma Virus; SRF, serum response factor; tBID, truncated BID; TCF, transcription factor; TLR, Toll-like Receptor; TUDCA, tauroursodeoxycholic acid