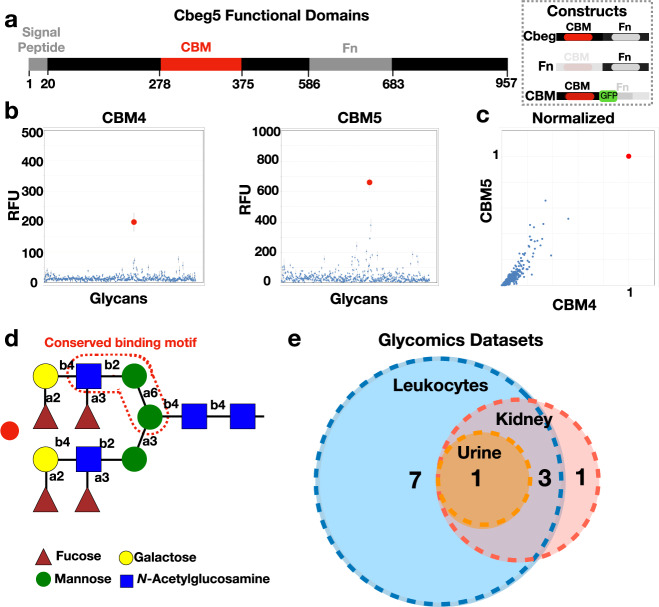
Fig. 1. Cbeg4 and Cbeg5 glycomics.
a Cbeg5 functional domains (InterPro) and protein constructs created for bioactivity assays (box). b Cbeg4 and Cbeg5 protein constructs were generated containing only the CBM domain and a GFP tag. The Cbeg5 CBM protein (CBM5) and the Cbeg4 CBM protein (CBM4) were assessed in a binding assay against a panel of 609 N-linked and O-linked glycans (Functional Glycomics Consortium). CBM5 and CBM4 were assayed at 5 μg ml−1 and 50 μg ml−1 in 6 replicates and glycan binding quantified as relative fluorescent units (RFU). Dot plots of CBM4 and CBM5 glycan binding screens at a concentration of 5 μg ml−1 (mean ± s.e.m). c Plot of CBM4 vs CBM5 glycan binding normalized to the top glycan binder (set at RFU = 1). Protein concentration is 50 μg ml−1. d The structure of the top bound glycan (red dot in b, c) is pictured. Analysis of CBM4/CBM5 bound and unbound glycans identifies a conserved binding motif outlined in red dotted line (glycopattern). e A Glyconnect search of glycomics datasets for samples containing the conserved N-linked glycan motif was performed. Glycan structures containing the conserved binding motif were most commonly identified in human leukocyte datasets (11/12 glycan structures). Four glycan structures were shared by human leukocyte, urine and kidney datasets. One glycan structure was exclusive to a kidney dataset.