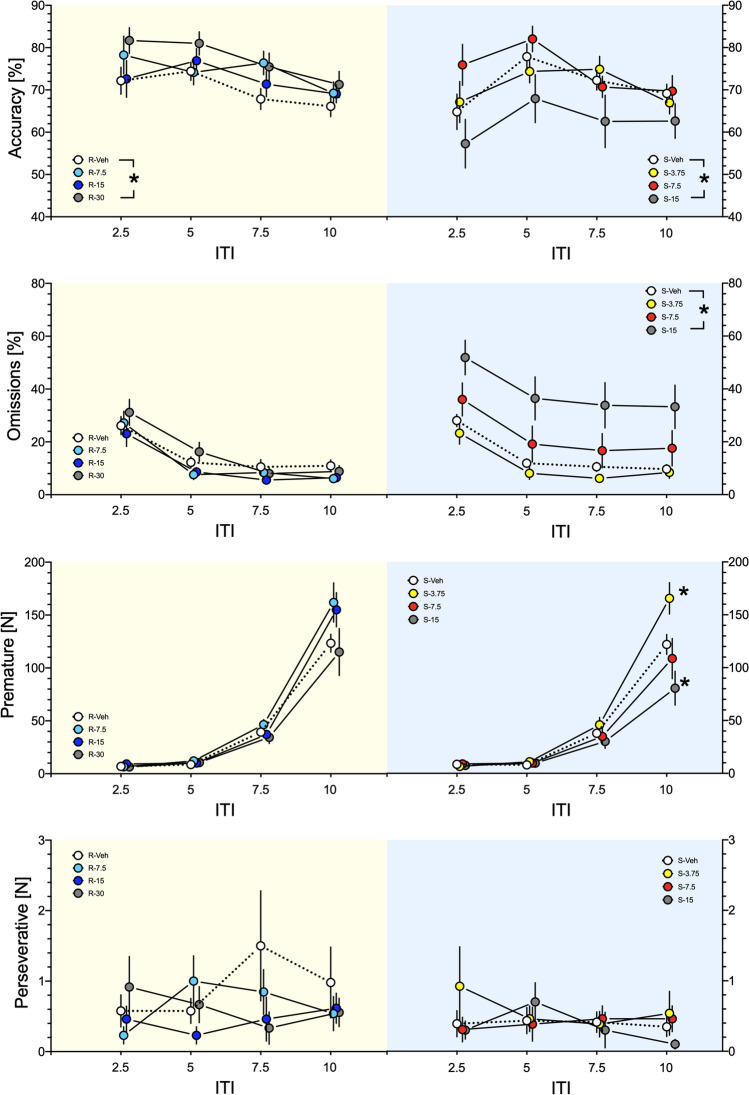
Fig. 5.
The top panel shows that while the highest dose of (R)-ketamine increased accuracy in 5-CSRTT, for (S)-ketamine, accuracies were decreased (*; P < 0.01–0.001, in legend), suggesting opposite effects of isomers on this measure of cognitive functions in variable ITI conditions. Panel close to top shows no effects of (R)-ketamine on response omissions but their increase by the highest dose of (S)-ketamine (*; P < 0.001, in legend), suggesting unspecific effects of this isomer. While premature responses were not affected by (R)-ketamine, (S)-ketamine in ITI of 10 s increased them at 3.75 mg/kg and decreased them at 15 mg/kg (*; P < 0.001; panel close to bottom), suggesting increased and decreased effects on impulsivity. Neither compound affected perseverant responses (bottom panel). Data represent mean ± SEM. Yellow backgrounds indicate the effects of (R)-ketamine; blue backgrounds of (S)-ketamine