Figure 6.
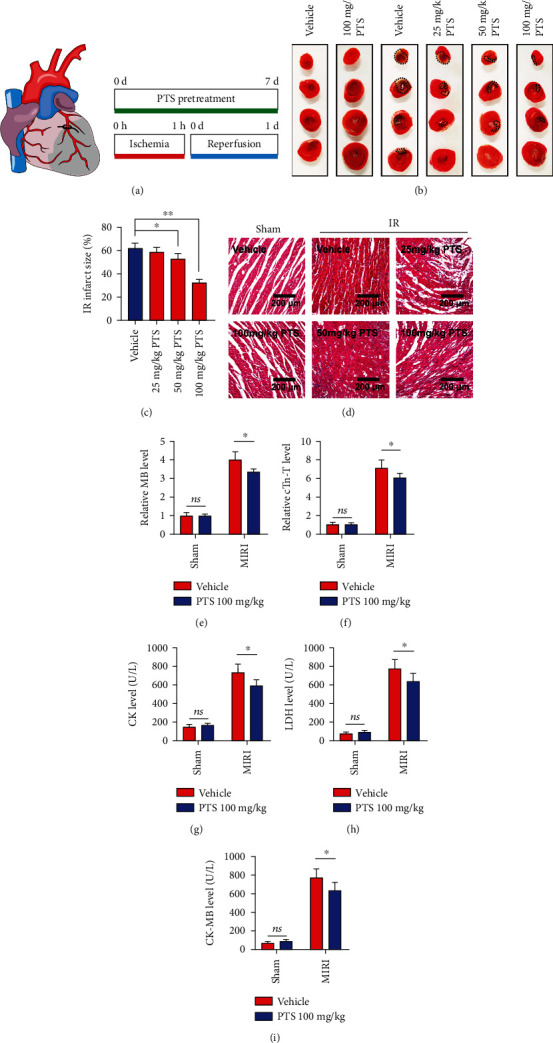
PTS attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI) in rats. A total of 60 rats were divided into six groups to determine the optimal concentration of PTS to treat MIRI rats, including the I/R group, sham group, sham+PTS group, and I/R+PTS groups (intragastric administration of 25, 50, or 100 mg/kg/d PTS aqueous solution followed by I/R operation). The pretreatment was carried over 7 days. The sham and I/R groups were pretreated with vehicle (water) before the operation. (a) Schematic diagram showing the position of the LAD branch and establishment of the I/R model. (b) Representative images of TTC staining. (c) Infarct size (black dotted circle) was quantified using ImageJ software. (d) Representative images of H&E staining of rat myocardial tissue sections. (e–i) The myocardial injury markers MB, cTn-t, CK, LDH, and CK-MB were quantified using ImageJ. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 8). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01. ns: not significant. AST: aspartate aminotransferase; CK: creatine kinase; cTn-T: cardiac troponin-T; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; MB: myoglobin.
