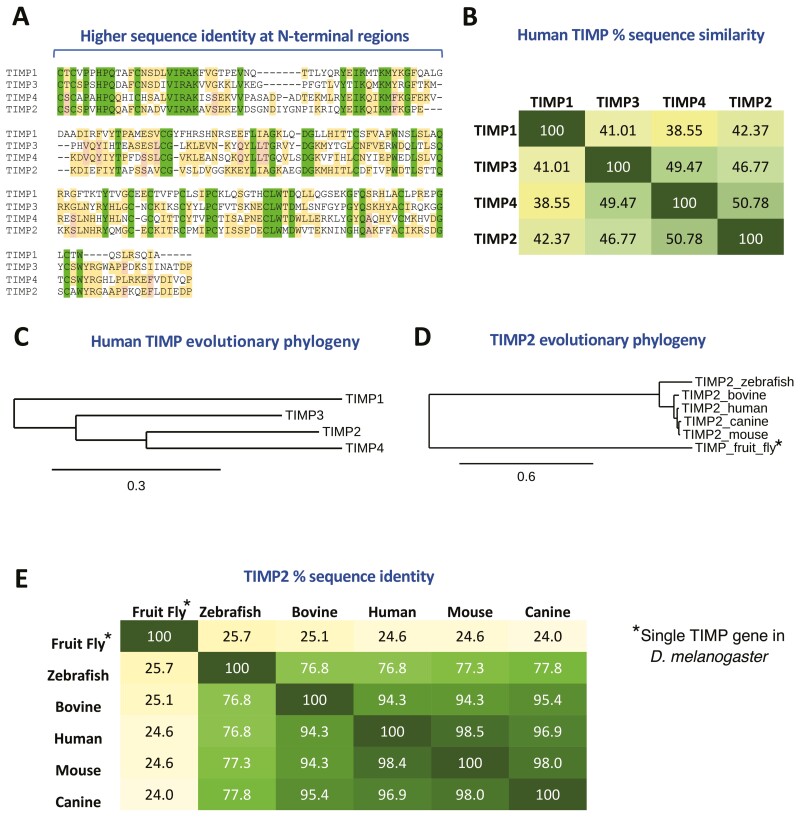
Figure 1.
TIMPs are a highly conserved family of endogenous proteins.
(A) Sequence comparison of the TIMP family identifies a largely conserved family with high sequence identity at their N-terminal regions (fully conserved residues highlighted in green), emphasizing their redundancy in action with regards to metalloproteinase inhibition (TIMP alignments are presented in order of their phylogenetic relationships, see Panel (C)). (B) Percentage sequence identity across the human TIMP family. (C) Evolutionary phylogeny across human TIMP family shows that TIMP1 is the most unique in terms of sequence identity and phylogenetic analysis suggests that it has the most ancient direct ancestor of the human TIMPs. (D and E) TIMP2 sequences are highly conserved, even showing around 25% identity with the single fruit fly (D. melanogaster) timp gene. Phylogenetic analysis was performed through http://www.phylogeny.fr/, using “One-Click” mode (see additional information).