FIGURE 2.
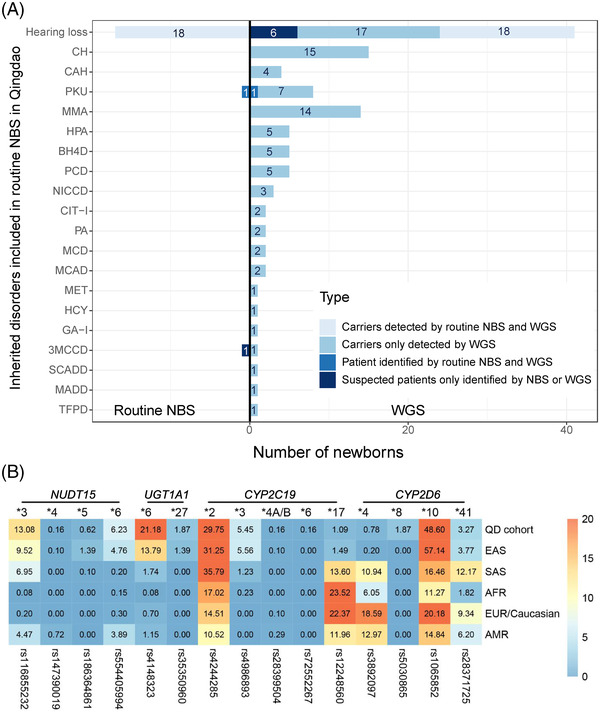
(A) Comparison between the findings of newborn WGS and routine NBS in the Qingdao cohort (n = 321). The findings of routine NBS tests are summarized on the left side of (A). In total, 18 carriers of hearing loss associated genes, one patient with PKU and one false positive result of C5‐OH were detected by existing routine methods. The findings of WGS are shown on the right side of (A). The WGS results confirmed the positive routine NBS findings of 18 carriers of hearing loss and the case with increased level of Phe. However, the infant with a routine NBS showing an increased level of C5‐OH (sample ID 18110806) was found to carry one pathogenic mutation in MCCC1, corresponding to being a carrier of 3‐methylcrotonyl‐CoA carboxylase deficiency (3MCCD). The newborn WGS also identified more infants carrying extra hearing loss mutations that were not identified by the routine NBS method, including 2 newborns carrying compound heterozygous P/LP variants in GJB2, 4 newborns harbouring a pathogenic mutation in MT‐RNR and 17 additional carriers harboured altogether 19 variants. Moreover, newborn WGS identified 59 extra carriers carrying 66 P/LP variants corresponding to 18 inherited metabolic diseases that could not be identified by the routine NBS tests. The abbreviations of diseases and the summary of are listed in Table S1. (B) Comparison of allele frequency of actionable PGx variants between the Qingdao cohort and five subpopulations of the 1000 Genome Project dataset, including East Asians (EAS), South Asians (SAS), Africans (AFR), Europeans (EUR) and Americans (AMR). In most cases, the allele frequency of the Qingdao cohort is consistent with the EAS, but differed significantly with the SAS, the AFR, the EUR and the AMR, such as CYP2C19*2, CYP2C19*3 and NUDT15*6. It should be noted, however, that three common PGx variants in the Qingdao cohort, CYP2D6*10 (48.60%), NUDT15*3 (13.08%) and UGT1A1*6 (21.18%), showed significant frequency differences with the EAS (p < 0.05), indicating population diversity within the East Asians. Notably, two rare variants, CYP2D6*8 (1.87%, n = 11) and CYP2C19*6 (0.16%, n = 1) which have not been reported in any subpopulation in the 1000 Genome phase 3 dataset and were first detected in our Qingdao 321 newborns
