Figure 2. Calcium stores in an excitatory presynaptic terminal.
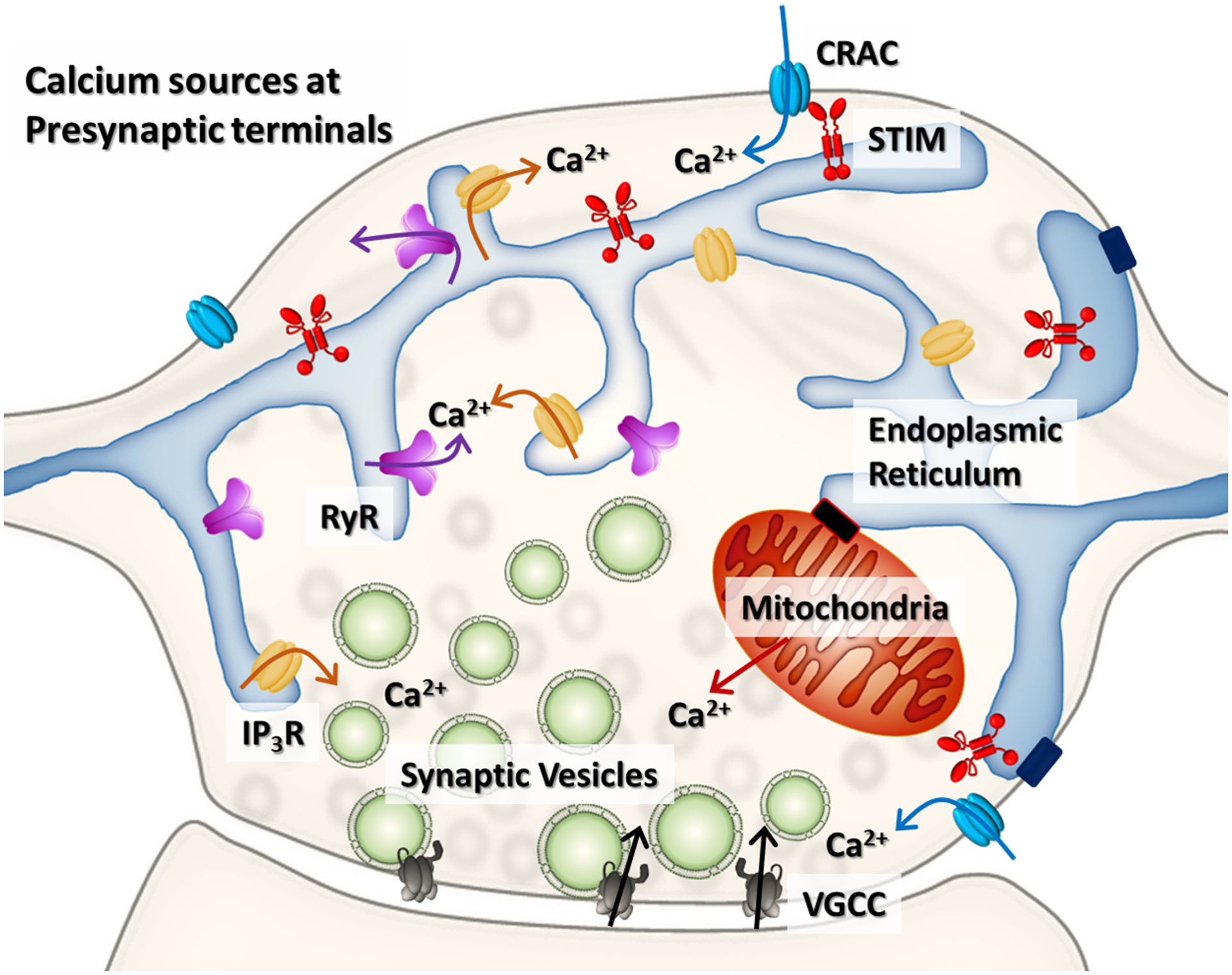
Action potentials gate the opening of VGCC with the consequent influx of extracellular calcium and the synchronized exocytosis of synaptic vesicles. The ER is the main intracellular source of calcium in axons. Calcium can be released via IP3Rs and RyRs during CICR, amplifying action potential-driven signals and neurotransmitter release. The SERCA sequesters calcium into the ER modulating calcium levels in the bouton. When calcium is depleted in the lumen of the ER, SOCE is triggered via STIM-CRAC interaction resulting in calcium influx into the terminal, which augments neurotransmitter release. Mitochondria can also work as a calcium source and a calcium sink (not discussed in this article).
