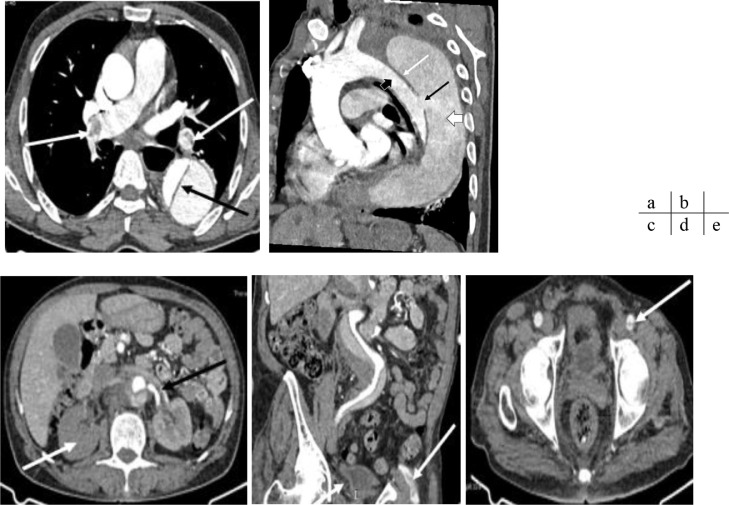
Fig. 3.
CT angiography of the chest and abdomen, axial slice (a, c, and e); sagittal (b) and coronal (d) reformation. Massive bilateral proximal pulmonary embolism (white arrows), aortic dissection (black arrow). Stanford type B aortic dissection with an entry point in the descending thoracic aorta (black arrow); the intimal flap (white arrow) separates the true lumen (black arrow head) from the false lumen (white arrow head). The false lumen is circulating and partially thrombosed. The dissection extends to the left renal artery, which is dissected (black arrow) the right renal artery emerges from the false lumen with right renal infarction (white arrow). The exit points are located in the right common iliac artery and left common femoral artery (white arrows). Aneurysmal dilation of the thoracic-abdominal aorta measuring 76 mm in maximum diameter at the thoracic level and 56 mm at the abdominal level, depending on the false lumen, extending from the aortic arch to the suprarenal aorta.