Figure 8. HMWH-induced anti-hyperalgesia signaling pathway.
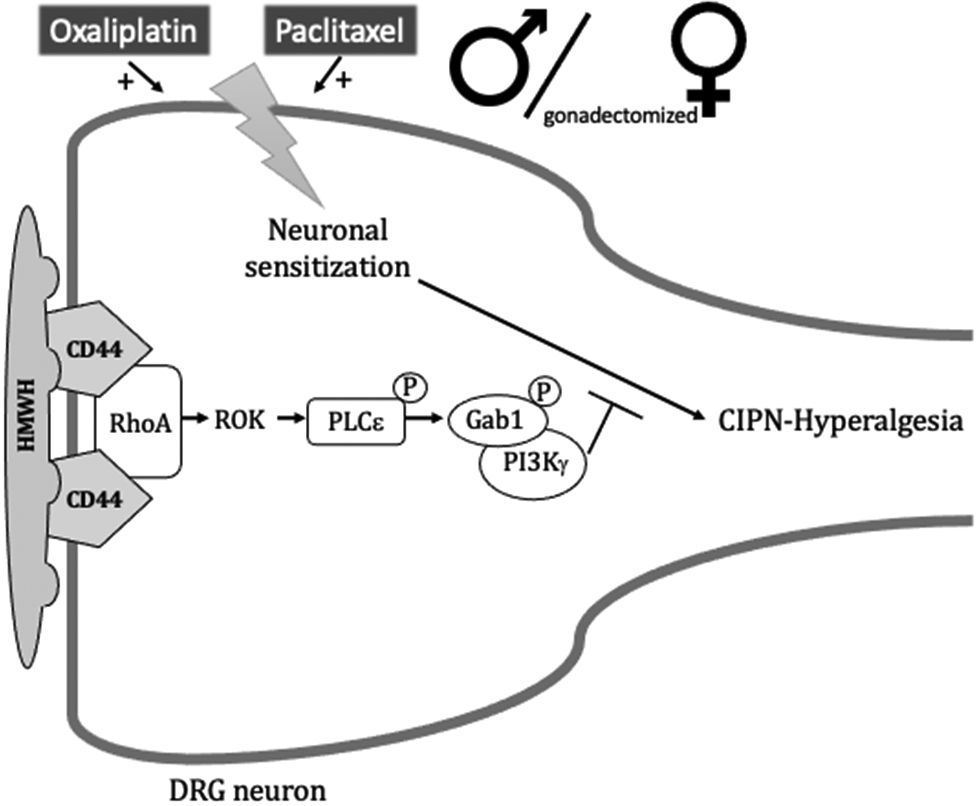
In male and gonadectomized female rats, oxaliplatin and paclitaxel induces CIPN-hyperalgesia that is reversed by HMWH, which binds to CD44 to induce its clustering in cell membrane lipid rafts and initiate signaling in downstream second messenger pathways. After binding to CD44, HMWH can signal via RhoA and Rac1, which in turn, activate ROK and PKN, respectively, leading to phosphorylation of PLCε and PLCγ1, respectively. Binding of HMWH to CD44 also stimulates RhoA, which activates ROK to phosphorylate PLCε, increasing serine/threonine phosphorylation of the adaptor protein, Gab-1 and leading to activation of PI3Kγ. Abbreviations: CD44, cluster of differentiation 44 (hyaluronan receptor); Gab1, scaffold protein; HMWH, high molecular weight hyaluronan; PI3Kγ, phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase gamma; PKN, fatty acid-activated serine/threonine kinase; PLCε, phospholipase C epsilon; PLCγ1, phospholipase Cγ1; Rac1, Rho family of GTPases; RhoA, Rho family of GTPases; ROK, Rho-associated kinase.
