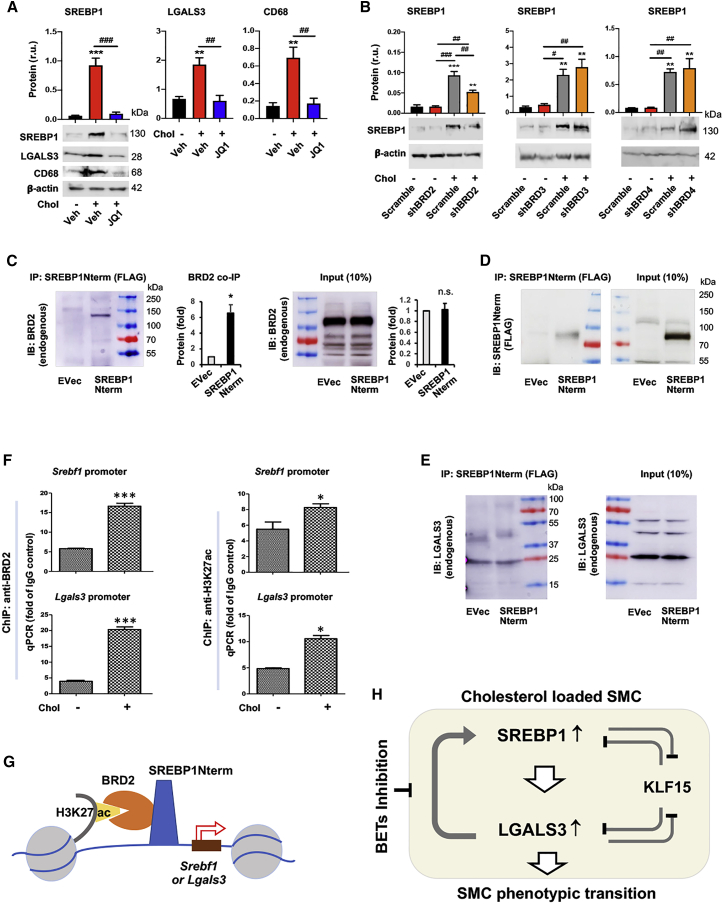
Figure 6.
BETs inhibition abrogates cholesterol-induced upregulation of SREBP1 and LGALS3 proteins
Mouse MOVAS cells were used unless otherwise specified. Cholesterol loading (80 μg/mL) and lentiviral transduction were performed as described in detail for Figure 1. Data quantification for western blots: mean ± SEM, n ≥ 3 independent repeat experiments. Data quantification for qPCR: mean ± SD, n = 3 replicates; presented is one of two similar experiments. Statistics: ANOVA followed by Tukey test; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 (between paired bars); ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, compared with the basal condition (the first bar in each plot). (A) Treatment of MOVAS cells with BET-selective inhibitor JQ1 abolishes cholesterol-induced protein upregulation of SREBP1, LGALS3, and CD68. JQ1 was added (final 0.5 μM) 2 h prior to cholesterol loading (final 80 μg/mL). (B) Effect of silencing individual BETs on SREBP1 protein levels in MOVAS cells. (C) Co-immunoprecipitation (coIP) of endogenous BRD2 with SREBP1Nterm. The vector for expressing FLAG-GFP (EVec control) or FLAG-SREBP1Nterm was transfected into HEK293 cells. An anti-FLAG antibody was used for IP, and coIPed endogenous BRD2 was detected via immunoblotting (IB). Mean ± SEM was calculated from n = 4 independent repeat experiments. Pre-stained marker bands are labeled with molecular weights. (D) IB of IPed FLAG-SREBP1Nterm. The same samples from (C) were used. (E) Lack of coIP of LGALS3 with SREBP2Nterm. Experiments were performed as in (C) except for the IB detecting endogenous LGALS3. (F) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) followed by qPCR. MOVAS cells were cultured without or with cholesterol (80 μg/mL) for 1 h prior to harvest for ChIP-qPCR. The value from IgG control was used for data normalization. ChIP was performed using an antibody specific for endogenous BRD2 or H3K27ac. Primer 2 was used to detect Srebf1 promoter; primer S1 (within the sequence of S1 site) was used to detect Lgals3 promoter (see Table S6). (G) A schematic depicts co-occupancy of BRD2 and SREBP1 at the Srebf1 or Lgals3 promoter, as suggested by the results presented in Figure 6 (A–F). (H) A schematic depicts the feedforward interplay of the SREBP1/LGALS3 dyad, as suggested by the results presented in Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 and this figure. SREBP1 positively regulates LGALS3 expression and vice versa. They each suppress KLF15 protein levels, and KLF15 negatively regulates their expression. Pre-treatment with BET-selective inhibitor JQ1 abrogates cholesterol-induced SREBP1/LGALS3 protein upregulation.