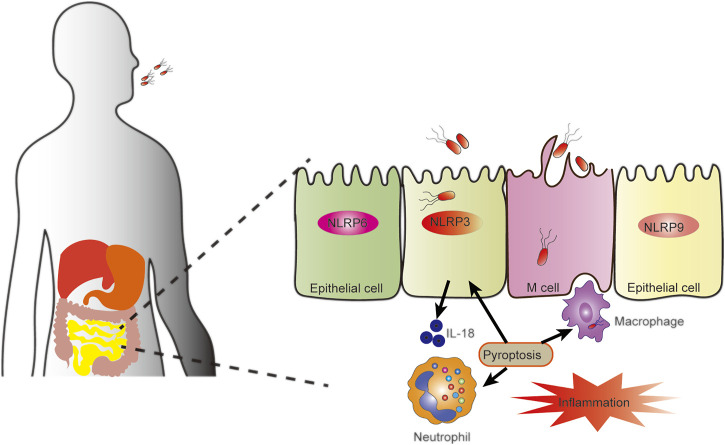
FIGURE 2.
Pyroptosis against intestinal pathogens. Pyroptosis plays a role in interactions between pathogens and intestinal epithelial cells or resident immune cells maintain intestinal homeostasis and inflammation. When pathogens invade epithelial cells, inflammasomes in the epithelial cells, including NLRP3, NLRP6, and NLRP9, are activated to secrete cytokine IL-18. The activation of the inflammasome in epithelial cells can also cause pyroptosis, ultimately leading to the release of bacteria that have invaded epithelial cells, stimulation of the immune response, and enhanced mucosal immune defense.