Table 2.
Summary of the effects of various pharmacological CBS inhibitors in cancer models.
| CBS inhibitor compound | Name | hCBS IC50 | Characteristics | Effects in cancer models |
|---|---|---|---|---|
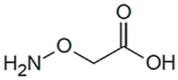 |
AOAA | 8 μM | PLP-dependent covalent inhibitor; inhibits multiple other enzymes as well | Efficacy in a cellular model in vitro and in murine models in vivo |
| AOAA methyl ester AOAA isopropyl ester |
YD0171YD0251 | 8 μM (with better cell uptake) | After hydrolysis by esterases, it yields AOAA and exerts similar effects as AOAA at lower concentrations/doses. | Efficacy in a cellular model in vitro and in murine models in vivo |
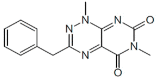 |
CH004 | 2 μM | Competitive inhibitor, identified by HTS, has known or likely off-target effects | Efficacy in a cellular model in vitro and in murine models in vivo |
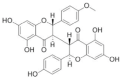 |
Sikokianin C | 3 μM | Competitive inhibitor, identified by HTS, has known off-target effects, not druggable | Efficacy in a cellular model in vitro and in a murine model in vivo |
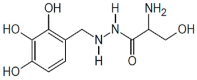 |
Benserazide | 30 μM | PLP-dependent covalent inhibitor; known clinically used drug – may be a possible candidate for drug repurposing | Efficacy in a cellular model in vitro and in murine models in vivo |
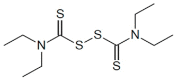 |
Disulfiram | 1 μM (after conversion to CuDCC) | Covalent inhibitor via copper; known clinically used drug with multiple MOA's – may be a possible candidate for drug repurposing; currently in several cancer clinical trials (but the proposed mechanism of action that is unrelated to CBS) | Efficacy in a cellular model in vitro and in murine models in vivo |
| Various polyphenols | [Multiple] | 5–30 μM | Multiple targets, most of them natural compounds | No information |
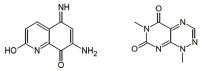 |
NSC11041 NSC67078 |
4–10 μM | Partially characterized compounds from various HTS campaigns; CBS selectivity and cell uptake insufficiently characterized | No information |
