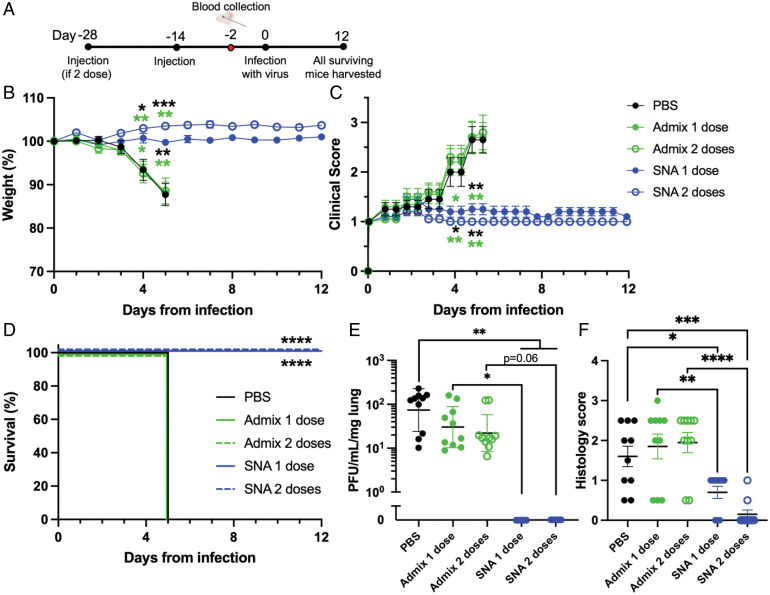
Fig. 5.
Vaccine effectiveness was tested using k18-hACE2 transgenic mice in a live viral SARS-CoV-2 challenge study. (A) Female and male mice (n = 10 total per group, 5 of each gender) were treated with vaccine or used as control groups and infected with virus as per the schedule. (B) Vaccination with SNA of either one or two doses prevented any body weight loss, (C) improved clinical scores, and (D) prevented any mortality as compared to vehicle mice (PBS) or admix mice treated with one or two doses when infected with SARS-CoV-2. On the date of death, lungs were harvested and assessed for (E) viral load and (F) histopathology. (E) No detectable virus was observed for SNA mice treated with one or two doses. (F) Scores of neutrophil infiltration were lower in mice treated with SNA vaccine compared to mice treated with admix vaccine or untreated. Comparisons were made between PBS and all other groups, and admix 1 dose versus SNA 1 dose, and admix 2 dose versus SNA 2 dose. For B and C, statistical significance is shown above the date at which the analysis was performed. Colors correspond to the group that SNA was compared to. Only significant comparisons were shown, and comparisons were made between SNA and PBS or the admix group with the same corresponding number of doses. For B, C, and E, analysis was done using a Brown–Forsythe ANOVA followed by a Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. For F, analysis was done using an ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. D was analyzed using a log-rank test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.