Fig. 1.
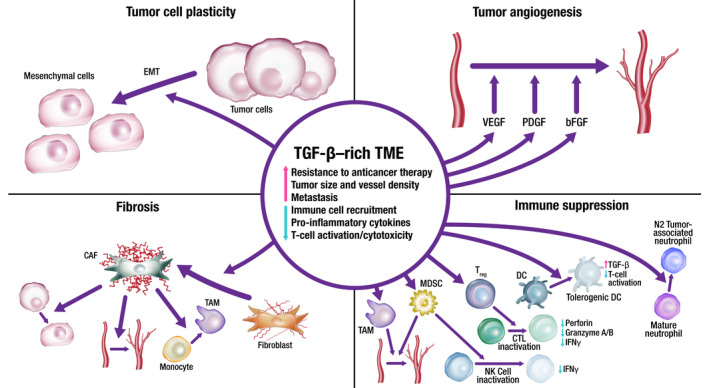
TGF‐β‐rich TME promotes survival mechanisms, including angiogenesis, immune suppression, fibrosis, and tumor cell plasticity. Through these mechanisms, TGF‐β signaling prevents antitumor immune responses, limits drug and immune cell access to the tumor, and promotes resistance to therapy. Through these processes, TGF‐β also promotes invasion and metastasis. bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; CAF, cancer‐associated fibroblast; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; DC, dendritic cell; EMT, epithelial–mesenchymal transition; IFN, interferon; MDSC, myeloid‐derived suppressor cell; NK, natural killer; PDGF, platelet‐derived growth factor; TAM, tumor‐associated macrophage; TGF, transforming growth factor; TME, tumor microenvironment; Treg, regulatory T cell; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
